AlertNow
AlertNow is an incident management platform that provides alert monitoring, escalation policies, and on-call scheduling to quickly detect and resolve incidents.
Quick Start Guide
This guide shows how to configure basic settings in order to use AlertNow service.
Get started with these steps:
📑 Step 1: Set up Your User Profile
Set up your basic information and notification rules. Contact information, notification rules, user settings and additional information can be configured in Personal Settings.
For more information about setting up user profile, please refer to Personal Settings.
📑 Step 2: Set up Integrations
Set up the integration by selecting the tool or service you are using from the list of integrations provided by AlertNow. You can then add one or multiple integrations in order to receive alerts from those tools or services and manage them.
For more information about setting up integrations, please refer to Integrations.
📑 Step 3: Create a Service
Create a service to manage incidents that are created in the integration. Service is a unit for managing incidents and provides related information that easily allows users to view and access incidents, integrations, escalation rules, extension, maintenance history they need to manage incidents. So you can create and use a service to reflect your needs.
For more information about creating services, please refer to Services.
Introduction
What is AlertNow?
AlertNow is SaaS-based service incident lifecycle management platform that allows users to quickly detect and manage incidents that occurred by using alert monitoring, escalation policies, and on-call scheduling. The key features are as follows.

- Unified Incident Management
- Receive alert information occurred in multiple 3rd party monitoring tools.
- Remove unnecessary duplicated alerts based on customized rules and create incidents with necessary alerts.
- Effective Team Communication
- Send the alert when an incident occurred, to the person who can handle the incident at the right time.
- Quickly deliver the alert via channels (SMS, Voice Call, Slack, KakaoTalk, Jandi etc.) designated by the user.
- Incident Resolution Focused Escalation
- Set assignee, action and time to handle the incidents step-by-step.
- When an incident is not acknowledged or closed, it automatically escalates to the manager of the next step to handle the incident, which reduces MTTD (Mean-Time-To-Detect) and MTTR (Mean-Time-To-Restore).
AlertNow - Flow
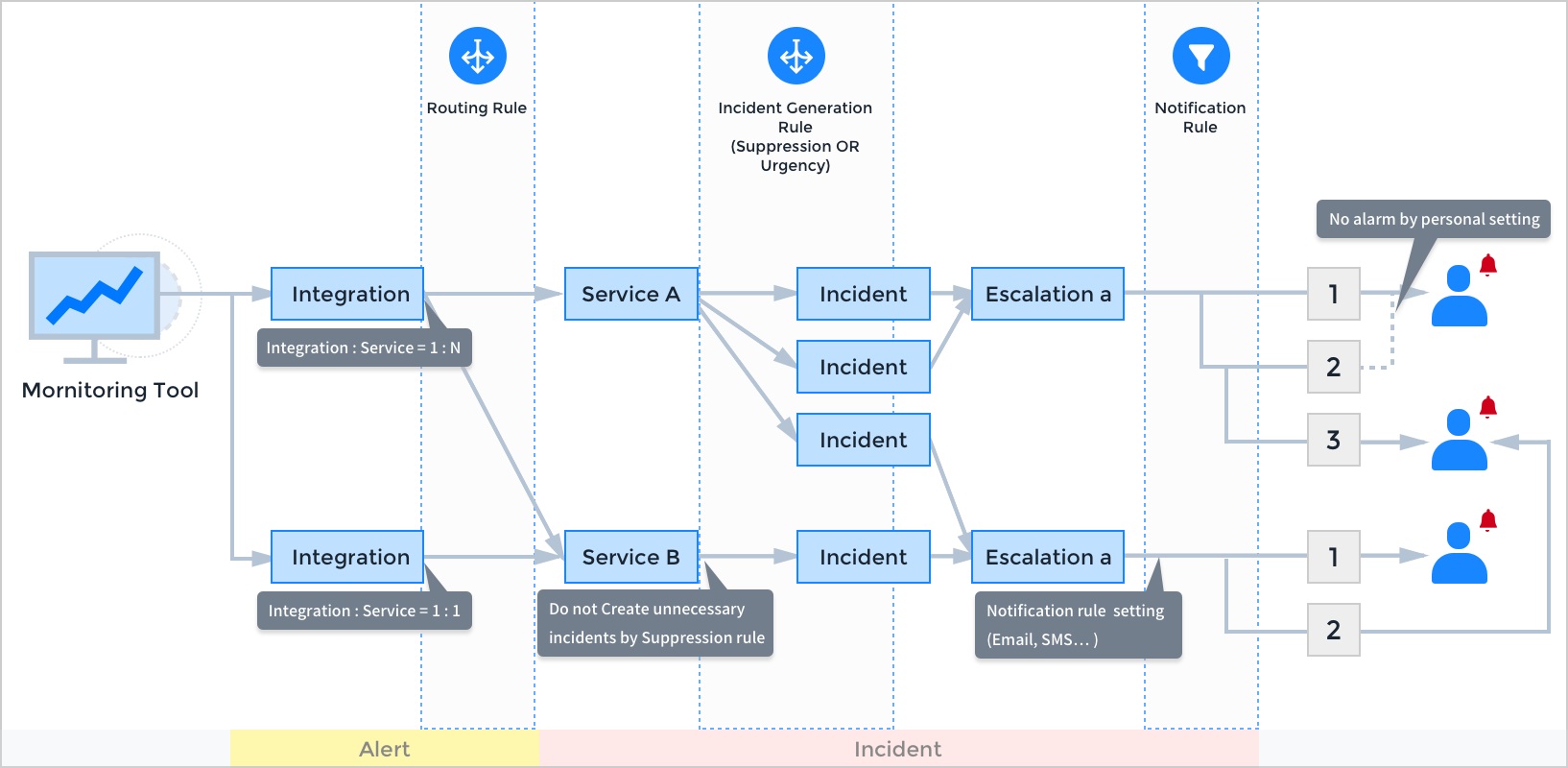
AlertNow - Setup Process

For Admin user, the setting steps are as follows:
Create Service → Create Integration → Create Schedule (Optional) → Create Escalation policy → Create Team (Optional) → Set Extension (Optional)
After completing the setting, alerts and incidents will be created according to information connected to integration. You can receive notifications about incidents created and status changed, and edit incidents accordingly.
AlertNow Key Terms
- Personal Setting: Users can set personal information and notification rules.
- Alert: It is raw data and the user cannot change or delete the data.
- Service: It is a unit to manage incidents occurred from integrations, and can be services or applications that users actually use and can be used freely for user’s convenience.
- Escalation: Users can manage incidents by setting managers to handle step-by-step and action and time.
- Extension: Users can export specific data created in AlertNow via external tools or services.
- Incident: When collecting alerts, it manages the status of the ticket created by incident policy.
- Integration: It is an endpoint that connects notifications occurred in 3rd party monitoring tools to AlertNow.
- Team: Users can use this service for managing all the information related to incidents such as escalations, users and services in a group.
Permissions by Role
You can view permissions by roles in the table and diagram below.
Permissions – Table
| Role | Feature | Integrations | Schedules | Extensions | Teams | Incidents | Services | Escalations | Users |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admin | Create | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Modify | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Delete | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| View | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Manager | Create | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Modify | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Delete | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| View | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Responder | Create | No permission | √ | ||||||
| Modify | √ | ||||||||
| Delete | |||||||||
| View | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Observer | Create | No permission | |||||||
| Modify | |||||||||
| Delete | |||||||||
| View | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
- Delete feature is not supported in Incidents and Users.
Permissions – Diagram

AlertNow Role
AlertNow provides 4 user types for user management and service usage.
※ Team and Schedule features are only available on the Enterprise plan.
Admin
Admin has the permission to access and manage the entire AlertNow service. Also, only admin users can create integrations and set service routing.
- For Admin user, the setting steps are as follows:
Create Service → Create Integration → Create Schedule (Optional) → Create Escalation policy → Create Team (Optional) → Set Extension (Optional) - After completing the setting, alerts and incidents will be created according to information connected to integration. Admin will receive notifications about incidents created and status changed, and edit incidents accordingly.
Manager
Manager has the responsibility for the service, and has the permission to create, view, edit and delete. However, the manager can view only in Integrations and Users features.
- For Manager user, the setting steps are as follows: Create Service → Create Schedule (Optional) → Create Escalation policy → Create Team (Optional) → Set Extension (Optional)
- After completing the setting, alerts and incidents will be created according to information connected to integration. You can receive notifications about creating incidents and changing status, and edit incidents accordingly.
Responder
Responder is the main assignee who receives incident notifications and solves problems accordingly, and create and view permissions for Incidents and Alerts; and only view permissions for Services, Teams, Schedules, Extensions, Escalations, and Users. However, no permission for Integrations.
- For Responder user, it is impossible to create escalation policy, but can be set as a responder for an escalation.
- After completing the setting, alerts and incidents will be created according to information connected to integration. You can receive notifications about creating incidents and changing status, and edit incidents accordingly.
Observer
Observer can check the problem-solving status if necessary. Has no permission for Integration; and only has view permissions for Incidents, Services, Teams, Escalations, Schedules, Extensions, and Users.
- Observer cannot receive notifications for creating incidents and changing status because it cannot be assigned to escalation responders.
Best Practices
Best Practices will allow you to get the maximum benefits of AlertNow.
When configuring responders for incident notifications: Sending notifications
Click Escalations menu.
![]()
Click [Create escalation policy] button.
![]()
Configuring Responders
If you want to send notifications, you can configure the registered user as a responder to receive notifications step-by-step.

Enter a name and description for the escalation policy.
Set the incident status to close escalations, Acknowledged or Closed.
![]()
Set how many times the escalation repeats, and up to 10 can be set for repetition.
![]()
In a responder input field, enter names of responders. Responders can be set as Schedules, Users and/or Teams (All members of team/Radom member of team), and multiple items can be selected.
![]()
Click [Repeat this step] to repeat the same step before escalating it to the next step. You can also set a number of repeated counts and intervals.
![]()
As shown in the figure below, if the interval is set as 30 minutes and no one takes any actions against the alert, this step will be escalated to the next step.
![]()
Click [Add an escalation stage] to add an escalation step. A maximum of 20 steps can be added, and each escalation step can be repeated as well. When you select the [Include responders of all the previous stages] checkbox, you can send notifications to all responders of all the previous stages.
![]()
Configuring Final Notification
If no one acknowledges or closes the notification after the escalation process is done, it sends the final notification to inform responders once again.

Select Use radio button to set the interval and count of final notification.
Click OK button to create an escalation policy and send notifications.
To receive notifications in various ways: Setting contacts
Registering Contacts
You can receive incident notifications via Email, SMS, WeChat, KakaoTalk, Telegram, Mobile app and Voice call.
Setting Contacts and Notifications
Click Personal Settings menu.
The Personal Settings screen consists of the following.
![]()
※ Refer to Personal Settings for more information.
Setting Additional Information
You can set basic information, role, and permission in the Additional Information page.
![]()
Click
![]() icon to set the time zone.
icon to set the time zone.The time zone setting popup will be displayed as below. If you select Custom Settings radio button, you can change the time zone. Click [OK] button to complete the setting.
![]()
Click
![]() icon to set your language. Select a language you want to use and click the check button.
icon to set your language. Select a language you want to use and click the check button.
![]()
To Minimize Management Overheads: Setting Incident creation rules
When a problem occurs, you can manage incidents efficiently by limiting unnecessary alerts, and classifying it by incident urgency.
Setting Suppression Rules
The alerts will continue to occur until the problem is fixed. If the user creates an incident for alerts that were created for the first time, incidents will not be created for the same type of incidents.
Click Services menu.
![]()
Click one of the created services and click Incident Creation Rules tab.
![]()
Click Modify button of the suppression rules and click the checkbox at the left.
![]()
After selecting the condition and duration, click OK button to create a rule. You can set the duration in seconds, minutes, hours, or days.
![]()
You can create only one rule at a time. You can deactivate the rule by clicking OK button in the popup window after disabling the checkbox.
Setting Incident Urgency
You can set the urgency for an alert, and check it by classifying created incidents by incident urgency.
Click Services menu.
![]()
Click one of the created services and click the Incident Creation Rules tab.
![]()
Click Modify button of the urgency rules and click the checkbox at the left.
![]()
Select the default rule of incident urgency. You can select the urgency from Highest, High, Medium, Low or Lowest.
If you click Add custom criteria checkbox, the custom rule will be applied over the default rule.
![]()
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Summary | Refers to Title in an incident list. |
| Alert Metric Name | In an alert detail screen, you will see the following when clicking View button. |
| It will also be displayed on the alert summary. | |
 |
Click OK after selecting the condition, entering the comparison value, and setting the urgency. Then, the urgency rule will be added accordingly.
Click OK button after disable the checkbox, then the rule will be deactivated.
Delay Creation Rules
Users can delay creating incidents for a number of times and periods for the same incident occurred consecutively.
Go to detail page in Service menu by click [Create Service] button.
![]()
In the detail page, choose Delay Creation Rules.
![]()
Set a number of times and time periods to delay creating incidents.
![]()
📑 You can find delayed incidents in the Alerts list in the Incidents.
When registering a service to be notified: Adding a service
Service is a unit to manage incidents that occurred in integration and can be managed by routing rules set in an integration.
Service Configuration

Creating in Service Menu
Enter a service name
Click Services menu.
![]()
Click button and enter a service name in the Create Service page.
Setting routing rules
You can receive notifications by classifying incidents based on routing rules.

Set the routing rule in the Create service page.
Select the created escalation from the Escalations menu in the Routing Rule.
If you click Add custom criteria checkbox, the custom rule will be applied over the default rule.
Select the escalation rule after entering the condition and comparison value.
Set the incident creation rules (Suppression Rule and Urgency Rule). Refer to the To minimize management overheads: Setting Incident creation rules for setting the creating rule.
![]()
Click OK button to create a service. The created service will be displayed as below.
![]()
Item Description Remark Incident You can check the Incident status by period and search condition. Integration You can check the integration information of the service. Escalation Rules You can check the escalation information of the service. Editable Incident Creation Rules You can check the incident creation rule of the service. Editable Extension You can check the extension information of the service. Editable Maintenance History You can check the history of adding and deleting maintenance schedules of the service.
When syncing with 3rd party monitoring services: Adding an integration
This chapter explains how to create Integrations.
Creating an integration
Click Integrations menu.
![]()
Click button.
![]()
Select the integration type to create an integration. For example, if you are using AWS CloudWatch for monitoring, click the AWS CloudWatch card.
![]()
Create integration page will be displayed as below.
![]()
Item Description Remark Integration Name Customers can set an Integration Name. | Required Integration Type The logo of the selected target is shown. Required
For creating a new service
When creating an integration, the service will also be created. You can create an integration in Create a new service page. Refer to the When registering a service to be notified: Adding a service for creating a service.
For selecting a service
When creating an integration, existing services will be mapped.

Select the default service rule.
If you click Add custom criteria checkbox and set the conditions (Alert Summary and Alert Metric Name), the custom rule will be applied over the default rule.
Click OK button after entering a name for an integration and selecting an existing service.
![]()
The URL is required information for connecting SNS (Simple Notification Service) and AlertNow. You can copy and paste the URL for creating SNS subscriptions.
To classify responders by tasks: Setting escalation routing
You can classify responders by setting conditions in creating a service.
Click Services menu to go to Services screen and select the created service.
![]()
Click Routing Rules tab from the service page, and set routing conditions.
![]()
Setting responders by region
- Click Add custom criteria checkbox, select
Alert SummaryandContainsand enter the region names in the comparison value field as below. You have to select the escalation after creating an escalation based on the conditions you set.
![]()
Setting responders by metric
Click Add custom criteria checkbox, and select ‘Alert Metric Name’ and ‘Contains’ in sequential order. Enter the metric names (ex: CPUUtilization) in the comparison value field as below. Select the escalation after creating an escalation based on the condition you set.
![]()
Click OK button after setting the escalation rules.
Setting responders by server roles (CPU, DB, Network)
Click Add custom criteria checkbox and select ‘Alert Summary’ and ‘Contains’. Enter the server roles in the comparison value field as below. Selecting the escalation after creating an escalation based on the condition you set.
![]()
Click OK button after setting the escalation rules.
Help
What is AlertNow?
AlertNow is SaaS-based service incident lifecycle management platform that allows users to quickly detect and manage incidents that occurred by using alert monitoring, escalation policies, and on-call scheduling.
Access AlertNow
After signing in, available services will be displayed on the left menu bar. Click AlertNow from the list to access.

Menu Configuration
The menu configuration of each AlertNow service is shown below.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Incidents | When collecting alerts, you can manage the status of the tickets created by incident policy. |
| Service | Service is a unit for managing incidents that occurred in Integration. |
| Schedules | Assign users to receive incident notifications in order to handle incidents more efficiently. |
| Escalations | When an incident occurs, you can manage as a rule by appointing a manager to handle it step by step and setting the action and time (timeout) to be processed. |
| Integrations | Endpoint that connects notifications occurred from 3rd-party monitoring tools to AlertNow. |
| Extensions | Export data that were created in AlertNow to external tools or services. |
| Teams | Service for managing all the information related to incidents such as escalations, users and services in a group. |
| Users | Assign users as managers, responders, or observers to handle incidents efficiently. |
| Change History | Provide history logs that were made in AlertNow. |
| Notification History | Provide a history of SMS and Voice calls sent by the AlertNow. |
| Report | Visualize incident-related data via graph and table in System report, Incident report, and Notification report. |
| Personal Settings | Customize personal information and notification rules to handle incidents efficiently. |
| Mobile App | Receive notifications on your mobile app, and acknowledge or close incidents. |
Incidents
Overview
The Incidents menu provides a list of alerts and incidents that occurred in each service. Using the Incidents, the user can identify problems that need to be handled and record the processing status of each issue.

Alert
If you receive notification events that occurred from monitoring tools or other services that were integrated with AlertNow such as Amazon CloudWatch and Microsoft Azure, the notification event will be created as an Alert.
- Alert is raw data and the user cannot change the data or delete the created alert.
- Incident is created based on alerts. Not all alerts are created as incidents, but only the ones that match the Incident creation rule.
- Users do not receive all the notifications directly. AlertNow creates the Incident with alerts, and sends notifications that need to be reviewed by the user.
Incident
When events are sent to AlertNow, an incident is created through a predefined Incident Creation Rule. After the incident is created, the user can record how the incident was processed or receive notifications through Escalation.
With incidents, you can proceed the followings:
- Set the maintenance schedule depending on certain cases such as releases, DB, Infra, or Security operations. During that time, an incident will not be created. The alerts occurred during the maintenance will be saved as “Suppressed (by maintenance)” so that no incident will be created.
- Create incidents manually even if no alerts have been created.
- Merge more than two incidents manually.
To prevent duplicate incidents from being created, Receiving Return to Normal Notification, Limit Unclosed Incident Creation, Suppression Rules, and Delay Creation Rules are provided.
① Receiving Return to Normal Notification

For incidents created based on the threshold, when the instance status gets back to normal, it automatically closes the existing incidents.
② Limit Unclosed Incident Creation
If there are unclosed incidents with the same CloudWatch alert name and dimension, it suppresses the incident creation.

📑 Note: Dimensions provided by CloudWatch
InstanceId, ApiName, Fleet, ServiceName, DistributionId, ClientId, RuleName, LogGroupName, ConnectionId, DBInstanceIdentifier, VolumeId, FileSystemId, LoadBalancerName, AutoScalingGroupName, ActionType, ClientId, PipelineId, JobId, Flow, StreamName, KeyId, FunctionName, BotName, MLModelId, Broker, HealthCheckId, Host, TopicName, QueueName, BucketName, AttackVector, LambdaFunctionArn, Domain, GatewayId, ServiceName, NatGatewayId,
VpnId, Rule, WorkspaceId
③ Suppression Rules
For alerts that are not filtered from “Unclosed incident creation limit”, it limits incident creation by applying the rules set from the service. If the conditions like Alert Summary and Metric Name occur repeatedly, you can set a period to avoid duplicate incidents from being created. However, there must be unclosed incidents to use suppression rules.
④ Delay Creation Rules
For recurring incidents, you can delay creating incidents until a specified time period and counts have passed. Enable this feature in the Creating Service of AlertNow page by second, minute, or hour (max. 1 hour), and at a maximum of 5 times for delaying the creation of incidents.
Alert and Incident relation
From what’s above, Alert and Incident can have the following relationships:
Based on Alert
Incident creation Alert : Created Incident [ 1 : 1 ] Triggered Incident Alert : Triggered Incident [ 1 : N ] Based on Incident
Alert based on creation Incident : Alert [ 1 : 1 ] Merge Incident Base Incident : Dependent Incident [ 1 : N ] Related Incident Incident : Related Incident [ 1 : N ]
Incident
Incidents > Incidents
The Incident provides a list of created incidents, so you can check the details of each incident and record the status of the process. It allows you to search specific incidents by filtering with period and keywords.
Screen Layout
The Incident menu is divided into two sections as below.

Incident List
You can check and search the list of incidents triggered. If you select the incident in the incident list, the information of the selected incident is displayed in the Details area. In the List screen, you can check the following information.Item Description Number Display the Identification Number of the incident. Title Display the title of the incident. Status Display the status of the incident, the values are as below. - Open
- Acknowledged
- Closed
Created Display the created date and time of the incident. Updated Display the last updated date and time of the incident. Urgency Display the urgency of the incident. Service Display the name of the service where the incident occurred. Assignee Display the name of the user designated as the manager of the incident. Incident Details
You can check the details of incidents selected in the Incident List. The user can also view on the bigger screen by enlarging it. In the Incident Details screen, you can check the following information.Summary
Item Description Service Display the name of the service where the incident occurred. Created Display the created date and time of the incident. Updated Display the last updated date and time of the incident. Urgency Display the urgency of the incident. Assignee Display the manager of the incident. Escalation Display the Escalation Rule set in the incident. Integration Display the name of the Integration that caused the incident. Integration Type Display the Integration Type that caused the incident. Indicator Alert Display the alert that caused the incident. Details
Item Description Message Display an attached message when an alert occurs. Description Display the description of the incident. You can enter the description manually.
Incident Status
Incident has three types of status values and the title area is displayed with different colors depending on the status.
Open
The incident is newly created and has not yet been processed.![Incident opened status]()
Incident opened status Acknowledged
The manager recognizes the problem and handles it.![Incident acknowledged status]()
Incident acknowledged status Closed
The problem has been solved and closed.![Incident closed status]()
Incident closed status
Incident Search
The user can search incidents by filtering with period and keyword in the Incident List. The search results are displayed in the Incident List.
Period Search
![Search Condition]()
Preset period selection
The user can search incidents by filtering the period and keyword in the Incident List. The search results are displayed in the Incident List.Preset Period All Search the entire period when incident occurred Today Select the current date Yesterday Select the yesterday’s date Recent 1 Week Select the recent 1 week based on the current time This Week Select the corresponding week based on the current time This Month Select the corresponding month based on the current time Last Week Select the previous week based on the current time Last Month Select the previous month based on the current time Custom
You can manually select the search start and end date/time by selecting Custom. When selecting a period, incidents within the selected period are displayed in the Incident List.
Keyword Search
The user can enter keywords to search for incidents. The search results will be displayed that matches with the keywords during the selected period.Toggle Button
![Status filter (Upper right)]()
Status filter (Upper right) - My Incidents
In the Incident List, it only displays incidents that you have been assigned. - All
Display all incidents
- My Incidents
Incident Management
You can perform the following tasks on Incidents.
Change status
You can change the incident status. You can change the status of an individual incident, and you can select multiple incidents to change the status.- Change Incident Status
Press the button at the bottom of the name to change the status in the details page.
![]()
- Incident in Open status can be changed to Acknowledged or Closed status.
- Incident in Acknowledged status can be changed to Closed status.
- Incident in Closed status cannot be changed.
- Change Incident Statuses in Batch
You can change all of the incident statuses at once by selecting multiple incidents and changing the status of all incidents. Select multiple incidents and change the status by clicking the Acknowledge or Close button on the upper left of the Incident List.
![]()
- Change Incident Status
Assign and Change Assignee
You can assign or change managers per incident. If you click the Assign button on the Incident Detail page, a popup will be prompted to assign a manager.Select Incident to assign manager
The Manager field displays the name of the currently assigned manager. If you click the Assign button, a popup will be prompted to assign a manager.
![]()
Select Manager
You can assign a manager by typing the name of the manager from the popup window. However, you cannot assign multiple managers for a single incident.
![]()
Write comment
You can write a comment on Incidents- Go to “Full screen” of the Incident page. In the Incident Detail screen, enter either in the “All” or “Comment” at the Activity History tab.
![]()
- Click Add button after entering a comment.
![]()
- Check the comment you entered.
![]()
- Go to “Full screen” of the Incident page. In the Incident Detail screen, enter either in the “All” or “Comment” at the Activity History tab.
- Change Title
You can change the title of each incident.- Click Modify button in the Title area of the full screen.
![]()
- Click OK button after editing the title.
![]()
- Check the title you changed.
![]()
- Click Modify button in the Title area of the full screen.
- Check Indicator Alert
You can check the indicator alert for each incident, and go to the Details screen of each alert.- Check incident indicator alert
![]()
- Click the indicator alert to view alert details
![]()
- Check incident indicator alert
Create Incident Manually
You can create an incident manually even before alerts were created.
- In Incident screen, click the Create Incident button.
Incident creation popup will be displayed as below.
![]()
The input items for creating an incident are as below.
Item Description Service Select a service created in the Service screen. Title Enter the incident title. Assignee If you hover the mouse over the input field, a list of assignees will be shown as a dropdown.
You can select the assignee from that list.
※ If you designate yourself for an assignee,- After creation, the incident status is automatically set as “Acknowledge”, so escalation may not be made.
(When setting an escalation rule, if the incident status to close escalation in Close condition is “Acknowledge”, escalation will not be made, but if the status is “Close”, escalation will be continued.) - In Personal Setting > Notification rules, the notification will still not be sent even if the notification in When an incident is assigned to me is set.
Escalation Default escalation rule
When selecting, the default escalation rules set in the service will be applied.Select an escalation rule
The user can select an escalation rule that has been manually created.Urgency Default urgency rule
When selecting, the default urgency rule set in the service will be applied.Select an urgency
The user can manually select the urgency. (None/Highest/High/Medium/Low/Lowest)Related Incident Add related incidents by searching the existing incident numbers. Description Enter the description about an incident to be created. - After creation, the incident status is automatically set as “Acknowledge”, so escalation may not be made.
- If you click OK button, incident will be created.
The created incident will be shown as below.
![]()
※ You cannot create an incident when there is no created service. You must create a service first in order to create an incident.

Merge Incidents
You can merge two or more incidents manually. To merge incidents, you need to specify the parent incident and dependent incident. Dependent incidents must be open or acknowledged. When merging incidents, the status of parent incident will not be changed, dependent incident will be closed and the status will be changed to ‘Closed (Merged)’. When the incidents are merged, all the notifications and escalations will be stopped.
Select incidents you want to merge, and click Merge button.
![]()
A popup will be prompted as below.
![]()
Select a parent incident to merge, and click OK button to complete merging incidents.
The merged incident will be shown as below.
![]()
Incident File Management
You can add, delete, or download attachments to Incidents in order to manage the incidents efficiently.
Select an Incident first and go to Attachment section.
![]()
In the Attachment page, you can drag and drop files or click Browse files button to upload the file.
![]()
When the files are uploaded, you can see the file list as below.
![]()
Select icons in the Manage tab to download or delete a file.
Alert
Incidents > Alerts
The Alerts menu provides a list of alerts and checks the details as well. You can also search for specific alerts by filtering with the period and keywords.
Screen Layout
The Alert menu is divided into two sections as below.
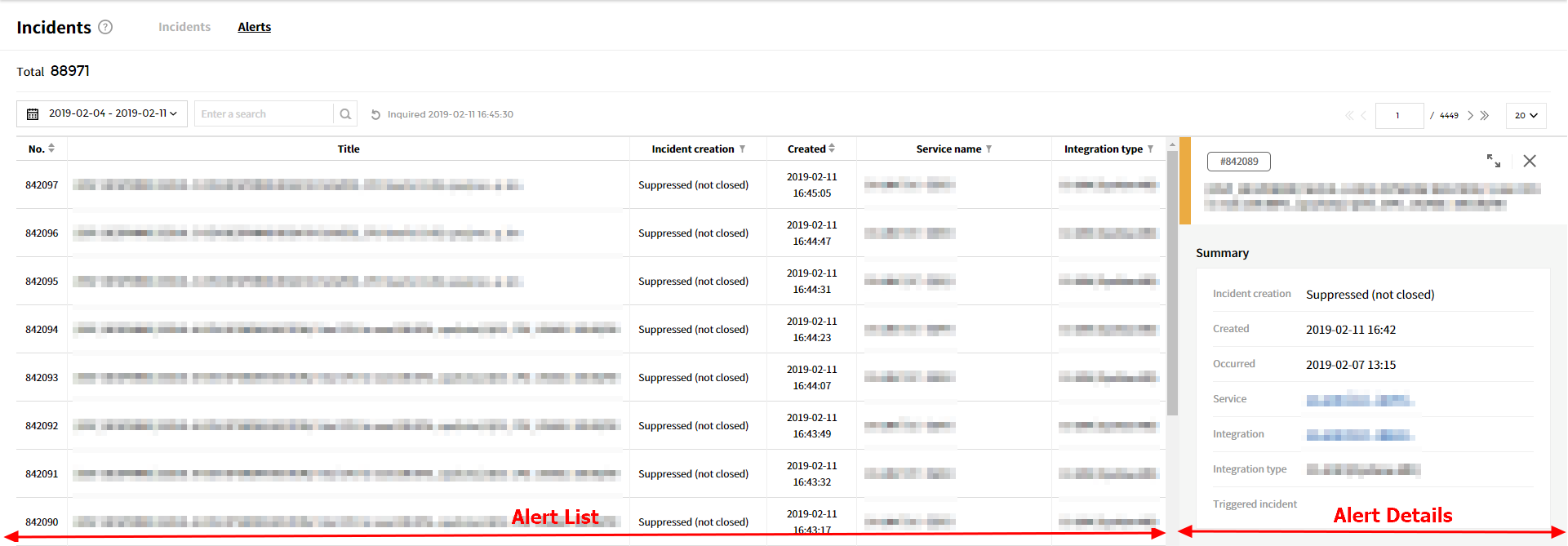
- Alert List
You can check and search alerts triggered from the alert list. If you select the alert from the list, the information about the selected alert will be displayed. In the List screen, you can check the following information.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Number | Display the Identification Number of the alert. |
| Title | Display the title of the alert. |
| Incident Creation | Display whether the incident for corresponding alert has been created. - Incident created - Suppressed (by suppression rule) - Suppressed (by maintenance) - Suppressed (not closed) - Suppressed (by delay rule) |
| Created | Display the created date and time of the alert. |
| Service | Display the name of the service where the alert occurred. |
| Integration Type | Display the integration type of the service where the alert occurred. |
Alert Details
You can check the details of the alert selected in the Alert List. The user can also view on the bigger screen by enlarging it. In the Alert Details screen, you can check the following information.- Summary
Item Description Incident Creation status Display Incident creation results according to Incident creation rule. Created Display the created date and time of the alert. Occurred Display the occurred date and time of the alert. Service Display the name of the service where the alert occurred. Integration Display the integration of the alert. Integration Type Display the Integration Type of the service that caused the alert. Triggered Incident Display the incident name where the alert occurred. - Details
Item Description Message Display a message when alerts were triggered. Description Description of the alert. You can write descriptions manually.
Alert Search
The user can search alerts by filtering with the period and keyword in the Alert List. The search results are displayed immediately in the Alert List.
Period Search
![Search conditions]()
Search conditions Preset period selection
Provide various period options for the user to choose. When the user selects a period option from the table below, the result will be displayed in the list immediately.Preset Period All Search the entire period when incident occurred Today Select the current date Yesterday Select the yesterday’s date Recent 1 Week Select the recent 1 week based on the current time This Week Select the corresponding week based on the current time This Month Select the corresponding month based on the current time Last Week Select the previous week based on the current time Last Month Select the previous month based on the current time Custom
You can manually select the start and end date/time by selecting Custom. When selecting the period, alerts within the selected period are displayed in the Alert List.
Keyword Search
You can search incidents by entering keywords. The search results will be displayed that matches with the keyword during the selected period.
Alert Management
You can perform the following tasks on Alert in the list.
- Check Message
You can check the detailed message about the alert that occurred.- Click Full Screen icon on the Alert Detail screen.
![]()
- Detailed message is displayed in the new tab.
- Click Full Screen icon on the Alert Detail screen.
Enter Description
You can write a description about the alert that occurred.- Click Full Screen icon on the Alert Detail screen. Then go to Description at the bottom of the detail page.
- Enter the description and click the check button.
![]()
- Check the description you entered.
![]()
- View Triggered Incident
You can check the incidents created by selecting an alert, and go to the Details screen of each incident.- Check Triggered Incidents
![]()
- Click the triggered incident to view Incident details
![]()
- Check Triggered Incidents
Services
Service is a unit for managing incidents that occurred in Integration, and provides all the necessary data about Incidents, Integrations, and Escalations, in a single page in order to manage incidents efficiently. Also, you can use routing rules that are set in integrations to manage incidents.
Service can be created in two ways:
Create Service from Menu
Select Service from the menu.
Click Create Service button.
Enter the required information.
| Item | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Service Name | Enter a name for a service that you want to create. | Required |
| Routing Rule | • Default Routing If the setting is to set to None, the default routing will be used. |
Required |
| Incident Creation Rule | • Suppression Rules If conditions like Summary and Metric Name occur repeatedly, you can add time conditions (Sec, ,Min, Hour, Day) to suppress repeating alerts. • Urgency Settings Set a level of urgency to handling incidents for optimal outcomes. • Delay Creation Rules Delay creating recurring incidents until a certain time period and counts. Time period can be set in second, minute, or hour, and the feature can be set at a maximum of one hour and 5 times. |
Custom Settings
① Choose the created service and go to the detail page, and select each tab to configure the settings.

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Incident | View incident status based on period and search conditions. |
| Integration | View the integration information about the service. |
| Routing Rule | View routing rules about the service, and can be edited. |
| Incident Creation Rule | View the incident creation rule about the service, and can be edited. |
| Extension | View the extension information about the service, and can be edited. |
| Maintenance History | View adding and deleting histories about the maintenance schedule. |
② In the Routing Rule tab, click [+ Add new rule] to open Routing Rule popup window. If the settings is set to None, Default Routing rules will be used. In addition, the person who creates the service will be assigned as the default responder.

③ Select Routing Rule to set alert conditions to receive notifications. For example, choose Metric Name and Contains as the condition and set CPU as the comparative value, you can receive alerts that match with these conditions.

● Metric Name by Integration
| Integration Name | Metric Name | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Cloudwatch | trigger.metricName | |
| Azure Alerts | context.condition.metricName | |
| Azure Alerts (Classic) | context.condition.metricName | |
| Datadog | alertMetric | |
| Google Cloud Monitoring | incident.condition_name | |
| Prometheus | None | |
| NewRelic | condition_name | |
| Jennifer5 | metricsName | |
| Grafana | None | |
| Sumo Logic | alertMetric Metric | • For Type Payload, extract metric values from searchQuery fields and use it as the alertMetric value (User must enter a metric value in the query to use it.) • Not used for Log Type Payload. |
| SAMS | ALM_CD_ID | |
| Nagios | alertMetric | • For Service Type Payload, use the serviceDesc field value as the alertMetric value. • For Host Type Payload, use the hostState field value as the alertMetric value. |
| Standard | metric_name | |
| Kapacitor | id | |
| SAMBA | metric_name | |
| Dynatrace | metricNm | • Use metricNm by combining in the form of entityName-ImpactLevel-EventType among the first Index data of problemDetailsJson.rankedEvents. |
| Elasticsearch Watcher | id | • No value to enter as a metric name. |
Create at Integration Creation
Click [Integration].
![]()
Then, click Create Integration button and select Amazon CloudWatch card.
[][integration_create]
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click the OK button to create the integration.
![]()
| Item | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Name | Enter a name for the integration. | Required |
| Integration Type | View the integration type that you selected. | Cannot be edited |
| Service | • Create New Service Service is created while creating Integration. |
Required |
| • Select Existing Service The existing Service is mapped while creating Integration. |
No duplicate selection | |
| Service Name | Enter a name for the service that you want to create. | Required |
| Routing Rule | • Default Routing Rule If there are no routing rules created, “Default rule” will be created. |
Required |
| • Add custom criteria The user can select Escalation based on the user-defined priority. The custom criteria will take precedence over the default rule. |
||
| Incident Creation Rule | • Suppression Rule If the conditions like Summary and Metric Name occurred repeatedly, you can add time conditions (Sec, Min, Hour, Day) to suppress repeating alerts. |
Optional |
| • Urgency Settings Set a level of urgency to handling incidents for optimal outcomes. |
Optional | |
| • Delay Creation Rules Set a time and count to delay creating recurring incidents. |
Optional |
- Select [Create New Service] or [Existing Service], and click [OK] button.
💡 Service can manage incidents by grouping multiple integrations and designating them as the service.
Set maintenance schedule
You can set up maintenance schedules depending on certain cases such as releases, DB, Infra, and Security operations. During the maintenance period, incidents will not be created. Two options are provided below to set up the schedule.
- Immediately Add Maintenance
It allows you to simply add a maintenance schedule immediately. The maintenance schedule will be started immediately by activating this feature.
Select the service you want to add the maintenance schedule in the Service menu.
![]()
In the Immediately Add Maintenance page, click one of the following: 5 mins, 15 mins, 30 mins, 60 mins.
![]()
A popup window will be prompted. Use the dropdown menu to change the duration, and available options are 5, 10, 30, 45, 60, and 120 mins.
![]()
Click OK button to immediately add maintenance schedule.
![]()
- Add Maintenance Schedule
It allows you to set a maintenance schedule manually. With this feature, the maintenance schedule will be started at the times you set.
Select the service you want to add a maintenance schedule in the Service menu.
![]()
In the Maintenance schedule, click [+ Add Maintenance Schedule].
![]()
Set the start time and end time, and enter the description if necessary, and click OK to add a maintenance schedule.
![]()
You can add up to 5 maintenance schedules for each service.
When you add the maintenance schedule, the schedule will be added to the service and you can check the status. Click Add time to change the time to close the maintenance in a different time, and click Terminate to close.
![]()
You can find the history of maintenance schedules at the Maintenance history tab.
![]()
Schedules
The Schedule feature allows you to assign users to receive incident notifications according to the schedule, which helps you handle incidents more efficiently. Using this feature, you can:
- Add multiple users in one schedule, and receive notifications regularly by setting rotation type.
- Manage various incident notifications as a single schedule by adding multiple layers.
- Another assignee designated by Override feature receives notifications for a certain period of time in case the original schedule assignee is absent.
To get started with the Schedules:
Click Configuration > Schedules.
![]()
The Schedules consist of the following.
![]()
| Screen Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| View Schedules Options | [My Schedules]: Only your schedules will be displayed. [All]: All the registered schedules will be displayed. |
| View | Set the period for viewing schedules. (1 day, 1 week, 2 weeks, or 1 month) |
| My Next On-Call | The next schedules for handling incidents will be displayed, and provided only on your schedule. |
| Layer | Display the assignee to receive incident notifications, period and override information. |
| Current On-Call | Display the on-going schedules. |
| Team | Display the teams using that schedule. If you select the team, it moves to the detailed screen of that team. |
| Escalation | Display the escalations using that schedule. If you select the escalation, it moves to the detailed screen of that escalation. |
Create Schedule
By creating a schedule, you can assign users to receive incident notifications, and set the shifts to receive notifications.
To create a schedule:
Click Create Schedule.
![]()
The creation screen will be displayed.
![]()
Enter a name of the schedule.
Select the time zone.
Select teams to include the schedule.
In [Responder Settings] of the Schedule Rule Settings, add assignees to receive incident notifications. The notifications will be sent by registration order. You can also change the order of notifications by dragging and dropping the newly added user to desired location, and delete the user by clicking X button.
![]()
In [Rotation Type Settings], the assignee added in a layer can set the shift period to receive notifications. You can select from daily, weekly, or custom.
![]()
If you enable [Restrict Reminder Time Option], you can limit the time and day to receive incident notifications. If you set it to [Daily], you will only receive notifications during the specified time of the day. If you set it to Weekly, you will only receive notifications during the specified day and time.
![If set to Daily]()
If set to Daily ![If set to Weekly]()
If set to Weekly Click OK to add a schedule.
※ You must add your schedule to escalations to use it properly. Schedules alone are ineffective for notifications.
Schedule Settings
You can modify schedules by adding or deleting layers, copy another schedule with the same condition, and delete them. On-going escalations cannot be affected by this modification, and incidents that occurred after the modification, changed schedule will be applied.
Modify Schedule
To modify schedules:
Click the created schedule and go to the details screen.
![]()
Click [Modify] on the menu icon.
![]()
Apply the changes in the modification screen. The items are the same as the ones for creating schedules.
If you click [+ Add a layer] button, you can add layers to the schedule. Up to 20 layers can be added.
![]()
To delete the specific layer from your schedule, click the Delete icon at the right of the layer.
![]()
Once you delete, the deleted layer cannot be recovered; and if modifying your schedule after deletion, it will automatically be excluded from escalation. Click OK button to delete a layer.
![]()
Click OK to modify a schedule.
Copy Schedule
To copy a schedule:
Click Copy on the menu icon at the top right of the details screen.
![]()
Existing schedule with the same settings will be copied ,and click OK to copy the schedule. The name of the copied schedule will be provided as {schedule name}-copy-{#} format.
![]()
Delete Schedule
To delete the schedule:
Click Delete on the menu icon at the top right of the details screen.
![]()
Click Delete button to delete the schedule. If the schedule has on-going escalations, it cannot be deleted.
![]()
Set Overrides
Override enables a user to take the on-call schedule for a specified amount of time. When an override is created, the specified user replaces the on-call user of the specified layers or all on-call users from all layers. You can select the range of layers, all layers or specific layers, to apply an override while creating the override.
Create Override
To create an override:
Click the created schedule.
Click Modify on the menu icon at the top right of the detail page.
![]()
Click Override on the menu icon in the modification page.
![]()
You can also create an override by selecting a timeline bar and clicking Create Override button in the popup window.
![]()
The Create Override popup will be displayed as below.
![]()
Enter a user name to assign as an overrider.
Select the range of layers to apply an override.
Select the time zone.
Set the start and end time to substitute the schedule.
![]()
Click OK button to create an override schedule.
Delete Override
To delete an override:
Select the override timeline bar, and click Delete Override button in the popup window.
![]()
In the popup window, check the override schedule to delete and click Delete button.
![]()
When the range of layers is set to all and the override is deleted, it will be deleted from all layers.
Escalations
Escalation allows you to set managers to be notified and actions to be taken in each step to handle incidents, and set the time limit if the incident is not acknowledged or resolved, it will be escalated to the next level.
Create Escalations
Select Escalation menu and click Escalations button.
![]()
Click [Create escalation policy] button.
![]()
Enter the required information and click [OK] button.
![]()
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter a name for the Escalation policy you set. |
| Description | Enter a description about the escalation. |
| Close Condition | Option to acknowledge or close the incident. If the policy is selected, the close condition is required. |
| Notification per Step | • Specify recipients to be notified for each step. • Up to 20 escalation steps can be added. • Escalation execution: Set a number of escalations to be executed. • Responder: Set a recipient to receive notifications. • Execute next step: When no action was taken on the alert for the specified time, it escalates to the next level. • Repeat this step: With this option, you can repeat the same step and set the number of times to repeat. • Interval: You can set a time period that should be passed before the incident escalates to the next level if no one acknowledges or closes. The interval can be set in minutes. If the policy is selected, the interval is required. |
| Final Notification | • The final notification will be sent to all recipients when no one responds to the alert after all the escalation policies are completed. • Enable the Use button to set the interval and number of times the final notifications should be sent. |
- Click [OK] button to create an escalation policy.
![]()
🏮 Escalation rules can be set in more details in Service and Integration by configuring Routing rules.
Add Responders
You can specify responders to receive notifications. Each escalation step can have one or more of the following as its responders:
① Users
② Schedules
③ All members of team
④ Random member of team

When Random member of team is selected, a member will be randomly selected. The same member can be selected as a responder again if Random member of team is selected in other steps as well.
📑 Under the Free, Basic, and Standard plans, Team* feature is not included. Please upgrade to the Enterprise plan to use this option.
Integrations
You can forward and manage notifications occurring in the tool with AlertNow by selecting the tools or services you are using from the list of integrations provided by AlertNow.
Configure Integrations
Click Integrations.
![]()
Click Create Integration button.
![]()
Select an integration type you want to use.
![]()
Fill out all required fields to create an integration.
![]()
The input items for the Integration settings are shown below.
| Item | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Name | Users can set a name of an Integration. | Required |
| Integration Type | The logo of the selected target is shown. | Cannot enter or edit |
| Service | - Create New Service When creating integration, a service is also created. |
Required |
| - Select Existing Service When creating integration, the existing service is mapped. |
No multiple selection |
The Create New Service screen is shown below.
![]()
Case Description Remark Service name Randomly enter a service name that the customer wants to create. Required Escalation Rules - Default escalation rule: If there are no created escalation rules, “Escalation basic rule” is created.
- Add custom criteria: The user can determine the priority and select escalation according to the conditions.
If selected, the rule of the condition set by the user takes precedence over the default rule.
Required Incident creation rules - Suppression Rule
If the condition items (Alert Summary, Alert Metric Name) occur consecutively,
you can set the period (seconds, minutes, hours, days) to prevent the creation of duplicate incidents. - Urgency Settings
You can set the urgency of Incident.
Optional
|Optional
Select Existing Service screen is shown below.
![]()
Case Description Remark Service routing rules - Select basic routing service.
- You can set the service routing by setting the condition items
(Summary, Metric Name) of Add custom criteria.
Required Click OK button at the bottom right to complete the addition.
Click the created integration to check the details.
![]()
The URL refers to SNS Webhook URL information to connect with AlertNow in SNS (Simple Notification Service) on AWS Console.If you create an integration in AlertNow and complete the required settings in each cloud service console accordingly, you will receive notifications when incidents occur.
Amazon CloudWatch
To connect AWS CloudWatch with AlertNow, you need to create an SNS topic in the AWS Console.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Amazon CloudWatch card.
![]()
In the Create Integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button.
![]()
Access AWS Console
From the AWS Console, type SNS, and then select Simple Notification Service.

Create Amazon SNS and Subscription
Select Topics in the Amazon SNS dashboard.
1. Create New Topic
Select Create topic located on the top-right of the screen. The Create topic screen will appear.

The table below provides descriptions for each item.
| Item | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Topic Name | It is a communication channel to send messages and subscribe notifications and used to create an ARN for later created Topics. |
|
| Maximum 256 characters. Can include alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-) and underscores (_). | Required | |
| - For example, CreateSNSTopicTest: ‘arn:aws:sns:us-west-2:111122223333:CreateSNSTopicTest’ | ||
| Display Name | It is the name displayed for your topic when subscribing to SNS. | Optional |
Click Create topic button.
2. Create Subscription
Select Create subscription located on the top-right of the screen.

Fill in the required input fields and click Create Subscription button.

The table below provides descriptions for each item.
| Item | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Topic ARN | It is automatically reflected based on the created Topic Name. | Editable |
| Protocol | Select HTTPS. | |
| Endpoint | Paste the URL for the integration created in AlertNow. | Required |
Click Create Subscription button.
3. Confirm Subscription
The subscription is being created.

Click Request confirmation button on at the upper right. Approval confirmation is made for the Subscription ID.

Move to RDS Console
In the AWS console, enter ‘RDS’ in the search field to go to Amazon RDS Console.
![]()
Select Event subscriptions at the left side of the screen.
![]()
In the Event subscriptions pane, select Create event subscription.
![]()
In the Create event subscription screen, enter a name for the event notification subscription. For Send notifications to, select an existing SNS ARN for a SNS topic, or select New email topic to enter a topic name and a recipient. Depending on the source type you selected, select the event categories and sources that you want to receive event notifications for.
![]()
Select Create. Select Create. Then, you can find that the subscription has been created.
![]()
Move to EC2 Console
Go to the EC2 Console to create an alert to connect to the AlertNow.
Step 1: Select Add/Edit Alarms
After selecting the corresponding EC2, select Action > CloudWatch Monitoring > Add/Edit Alarms as below.
![]()
Step 2: Create Alarm
![]()
Click Create Alarm button.The input items are shown below
![]()
Item Description Remark Send a notification to Find and select the created topic. Selection field Whenever Set the threshold value. Input field If you press the Save button, the following message will be shown.
![]()
Add Return to Normal Notification
What is “Receiving Return to Normal Notification”?
If incidents are created based on the threshold settings and the instance status gets back to normal, the incidents are automatically closed.

- Step 1: Select Add/Edit Alarms
After selecting the corresponding EC2, select Actions > CloudWatch Monitoring > Add/Edit Alarms as below.
![]()
- Step 2: Click “View” for alerts to set Return to Normal Notifications
![]()
- Step 3: Click Actions > Modify
![]()
- Step 4: Click Edit Alert > Actions below the alert definition > +Notifications
![]()
- Step 5: After adding notifications, set the condition to “State is OK” and save changes
![]()
- Step 6: Check setting changes
![]()
Microsoft Azure
To connect Azure Alert with AlertNow, you need to create the metric alert in the Azure Portal.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Azure Alerts or Azure Alerts (Classic) card for your needs.
![]()
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.


Adding Metric alert in Alert (Classic)
Go to Azure Portal. After logging in, click Monitor > Alert (Classic) as below.
![]()
Set Subscription, Source, Resource group, Resource type, Resource, and click + Add metric alert (classic).
![]()
Check the required input fields and click OK to create the metric alert.
![]()
![]()
| Item | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Enter the name. | Required |
| Description | Enter the description about a rule. | Optional |
| Source | Alert on: It is set to “Metrics” as default. | |
| Criteria | Subscription: The subscription set in the previous step is automatically selected. Resource group: The resource group set in the previous step is automatically selected. Resource: The resource set in the previous step is automatically selected. Metric: Select a metric. Condition: Set a condition about a rule. Threshold: Set a threshold about a rule. Period: Select the metric that you want this alert rule to monitor. |
Required |
| Notify via | Email owners, contributors, and readers: Select the checkbox if you want to send notifications via email. Additional administrator email(s): Enter the email address to send notifications. Webhook: Paste the Webhook URL information copied from Integration |
Required for Webhook |
For Microsoft Azure, Receiving Return to Normal Notification is enabled automatically, so no additional setting is needed.
Adding Alert rule in Alert
In Azure Portal, you can also connect Azure Alert with AlertNow by adding alert rules.
Go to Azure Portal. After logging in, click Monitor > Alert as below.
![]()
Set Subscription, Resource group, Time range, and click + New Alert Rule.
![]()
The Add Alert rule screen will be displayed as below. Click Define action group > + New action group.
![]()
The Add action group screen will be displayed. Set the action type to “Webhook”. Then, in the URI field of the Webhook window, paste the webhook URL information copied from Integration.
![]()
| Item | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Action group name | Enter the Azure Resource name. | Required |
| Short name | Enter the short name included in email and SNS notifications. | Required |
| Subscription | Select the subscription in which the group will be saved. | Required |
| Resource group | Select the resource group the group will be associated with. | Required |
For Microsoft Azure, receiving Return to Normal Notification is enabled automatically, so no additional setting is needed.
CA UIM
Depending on your country or region, this feature may not be available.
If you want to create CA UIM integration, you need to additionally set monitoring groups.
Click Create integration button. Then, select the CA UIM card.
![]()
Enter an integration name.
![]()
After entering the monitoring group name, click monitoring groups to add. Then, those groups will be added to Linked Monitoring Groups. If you click the X button next to the group name, that group will be deleted from the list.
![]()
You can either add or delete only the monitoring groups added in the Monitoring Dashboard > Configuration > Monitoring Group list.
![]()
Datadog
To connect Datadog with AlertNow, you must create a webhook and add a monitor in Datadog.
Click Create Integration button and then select the Datadog card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Creating Webhook
Go to Datadog website.
Click Integrations > Integrations at the left side of the screen.
![]()
If you click Integrations, a list of integrations supported in Datadog will be displayed. Click Webhooks integration.
![]()
Under the Configuration tab, enter Name and URL. The URL can be found in the detailed page of AlertNow console.
![]()
![]()
Select Use custom payload checkbox to choose whether to use custom payload.
![]()
- In the Custom Payload field, enter the custom payload information provided in AlertNow.
{
"id":"$ID",
"email":"$EMAIL",
"eventTitle":"$EVENT_TITLE",
"eventMsg":"$EVENT_MSG",
"textOnlyMsg":"$TEXT_ONLY_MSG",
"eventType":"$EVENT_TYPE",
"date":"$DATE",
"datePosix":"$DATE_POSIX",
"alertId":"$ALERT_ID",
"alertType":"$ALERT_TYPE",
"aggregKey":"$AGGREG_KEY",
"orgId":"$ORG_ID",
"alertStatus":"$ALERT_STATUS",
"alertScope":"$ALERT_SCOPE",
"hostname":"$HOSTNAME",
"user":"$USER",
"username":"$USERNAME",
"snapshot":"$SNAPSHOT",
"link":"$LINK",
"priority":"$PRIORITY",
"tags":"$TAGS",
"lastUpdated":"$LAST_UPDATED",
"lastUpdatedPosix":"$LAST_UPDATED_POSIX",
"alertMetric":"$ALERT_METRIC",
"metricNamespace":"$METRIC_NAMESPACE",
"alertTransition":"$ALERT_TRANSITION",
"orgName":"$ORG_NAME",
"alertQuery":"$ALERT_QUERY",
"alertTitle":"$ALERT_TITLE",
"alertCycleKey":"$ALERT_CYCLE_KEY"
}
- Click Update Configuration button.
Creating Monitor
Click Monitors > New Monitor at the left side of the screen.
![]()
Select the monitor type.
![]()
Enter the monitor name in Say what’s happening step.
![]()
In Notify your team, which is the final step, select the webhook you created and click Save button.
![]()
A list of created monitors will be displayed in Monitors > Manage Monitors.
![]()
New Relic
To connect New Relic with AlertNow, you must set Alert Condition and Webhook in New Relic.
Click Create Integration button and then select the New Relic card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Setting Webhook
Click Alerts > Notification channels > + New notification channel at the top of the screen.
![]()
Select the Webhook as a channel type.
![]()
Enter the following for creating a notification channel.
![]()
Click Create channel button to create a channel.
Click the created webhook. In Alert policies tab, click Add alert policies button.
![]()
Select alert policies to add and click Save changes button. The alert policies will be mapped to created webhook.
![]()
Setting Alert Condition
Go to New Relic and click INFRASTRUCTURE at the top of the screen.
Click Settings in the dashboard.
![]()
In Alerts screen, click Create alert condition button.
![]()
Creating alerts screen will be displayed as below.
![]()
Click Create button after completing the settings.
Adding Condition
Go to New Relic and click [APM] at the top of the screen. In the dashboard, you can check the applications that are running.
![]()
Click Alerts at the top of the screen. In the Alert policies screen, select a policy to add a condition.
![]()
Click Add a condition button.
![]()
New Condition screen will be displayed.
![]()
Click Create condition button after completing the settings.
![]()
Google Cloud Monitoring (GCP)
To connect GCP with AlertNow, you must add Webhook and Alert Policy in the GCP console.
Click [Create Integration] button and then select the Google Cloud Monitoring card.
![]()
In the [Create integration] page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Adding Webhook
Go to Google Cloud Console.
Click Monitoring located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Select Alerting in the Monitoring menu.
![]()
Click EDIT NOTIFICATION CHANNELS button in the Alerting page.
![]()
Click ADD NEW button from the Webhooks.
![]()
Enter Endpoint URL and Webhook name. For the Endpoint URL, you can copy and paste the URL created in AlertNow.
![]()
Do not select Use HTTP Basic Auth as AlertNow does not use it.
- If you click TEST CONNECTION button, Google Cloud Monitoring will check your URL. Once the verification is completed, “Test notification successfully sent” message will be displayed below and SAVE button will be activated. Click SAVE button to add a webhook.
![]()
Adding Alert Policy
Click CREATE POLICY button in the Alerting page.
![]()
Click ADD CONDITION button to set the condition for creating alerts.
![]()
Click NEXT button after adding the condition.
![]()
Select a notification channel and click NEXT button.
![]()
Enter the policy name and click SAVE button to add an alert policy.
![]()
Jennifer5
To connect Jennifer5 with AlertNow, you need to configure Event Rule and Adapter in the Jennifer console.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Jennifer5 card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Download Jennifer5 Adapter for AlertNow
To integrate Jennifer, click Download Jennifer5 Adapter for AlertNow to download. Jennifer 5 is not compatible with the Jennifer 4.5 version.
Event Rule Configuration
Sign in with Jennifer, and click Management button located on the top-right of the screen.
![]()
Select EVENT Rule from the popup window.
![]()
Select Metrics EVENT from EVENT Rule window, and click + Add button.
![]()
The table below provides descriptions for each event.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Error Event | Configure error events for agents and applications. |
| Metrics Event | To create metrics events, configure metrics values such as CPU and Memory of applications. |
| Compare Event | Create events by comparing past metric data. |
| e.g.) Issue an alarm if the memory usage exceeds 50% compared with the same time last week. |
- Select Target Type for rule settings.
![]()
The table below provides descriptions of target types.
- Each target type has different configuration metrics, and target items available for settings are listed below.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Instance | Provide resources metrics such as Memory, CPU, and Network |
| Business | Provide metrics data such as TPS and Response time per Business Group |
| Domain | Provide metrics data such as Bad Response, Visitors, and Instance per Domain Group |
- Select items required for rule settings and click Save button.
![]()
The table below provides detailed descriptions for metrics.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Rule | Enable or Disable an event by selecting On or Off button |
| Severity | Set severity for an event as NORMAL, WARING, or FATAL. It can adjust frequencies of occurrence of events based on the severity. |
| Comparison target | To create an event rule, input value (constant) by using integers and comparison operators, for example, ‘90 > value’ |
| Measurement time (sec)/Reference count | Issue events after comparison target created events that exceed the predetermined measurement time and reference count. |
| Icon Auto Recovery Time (sec) | Time to recover the status from failure to normal automatically |
| Enter Your Customer Message | Enter user-defined messages for issued events. This is not a required input field, but this message will be displayed along with other events that will occur in the future. |
| Script Auto Run | Automatically run user-defined script in the instance where target applications are running when events are issued. |
Configure Adapter
Click the Management button located on the top-right of the Jennifer screen, and select Adapter and Plugin.
![]()
Click one of events listed in the table from Adapter and Plugin popup window. The extended screen will appear displaying Classifications, ID, Path, and Class.
![]()
The table below provides descriptions for each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Classifications | Type of adapters, and must select Event for AlertNow. |
| ID | ID is a unique ID for configuring adapter, and must type in alertnow for AlertNow. |
| Path | It is the path where distributed adapter is located, and upload jenniferAdapter-1.0.0.jar file that you previously downloaded. |
| Class | It sets EventHandler, and use com.alertnow.jenniferAdapter.AlertNowAdapter that AlertNow provides. |
Click Option button after filling in the required information.
![]()
A popup window will be appeared where you can enter Webhook URL, and then click + Add button.
![]()
Input Key and Value, and then click Save button.
![]()
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Key | It is a unique value, and it doesn’t work as an identifier so that users can name it freely. |
| Value | Paste Webhook issued from AlertNow and add it. |
Notice: It is required to restart ViewServer after registering the Adapter. AlertNow allows you to add multiple Webhook.
EVENT Integration
Click Management button after completing the setup of Event rule and Adapter. Select EVENT Integration from the popup window.
![]()
Configure the severity and push types from EVENT Integration screen.
![]()
Notice: Normal must be selected in order to issue events. To select a push type, Main External Link should be On.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Main External Link (On/Off) | Enables or disables the feature to push all of the issued events by selecting the On or Off button. |
| Severity | Normal, Warning, or Fatal can be selected for pushing the predetermined event rule, and only selected severity will be pushed. |
- Schedule Off and Repeat Off functions from EVENT Integration screen. As shown in the figure below, click Management button to set these functions.
![]()
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Off Scheduling | Set “Start Time” and “End Time” for a certain period to turn off the Event Integration. |
| Repeat Off | Set “Start Time” and “End Time” on a daily basis to turn off the Event Integration. |
When Schedule and Repeat Off functions are set, it affects all events listed in the table.
SAMS
Depending on your country or region, this feature may not be available.
To integrate SAMS with AlertNow, you need to set up Full Path Text additionally.
Click Create integration button located on the top-left side, and select the SAMS card.
![]()
Enter an integration name.
![]()
Add to the Full Path Texts to Connect by selecting one or more items to connect from the All Full Path Texts. If you click X button next to the Full Path Text name, it will be removed from the list.
![]()
Fill in the required information in the Service field and then click OK button to create integration.
![]()
Prometheus
To connect Prometheus with AlertNow, you must configure Webhook in the Prometheus.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Prometheus card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Webhook Configuration
Go to Prometheus.
Click DOWNLOAD to install and configure Alertmanager that is required for this integration.
![]()
Create an Alertmanager configuration file. You can find an example configuration file on the GitHub.
Copy the URL created in AlertNow and paste it to Webhook to complete the configuration.
![]()
![]()
Grafana
To connect Grafana with AlertNow, you must configure Webhook in the Grafana.
1.Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Grafana card.

- In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Webhook Configuration
Sign in with Grafana, and click Notification Channels located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Click New channel button from the Notification Channels screen.
![]()
Enter a new channel’s name and select a type as Webhook. Then copy the URL created in AlertNow and paste it to url field in Webhook Settings. Click Save button to create a new channel.
![]()
![]()
Select Alert Rules located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Select the alert to connect and then add the created channel to Send to in Notifications to complete the configuration.
![]()
![]()
Sumo Logic
To integrate Sumo Logic with AlertNow, you must connect Webhook and add Monitor in Sumo Logic.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Sumo Logic card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Set up a Webhook Connection: Metric
Sign in with Sumo Logic, and select Manage Data > Collection located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Select Add > Add Source in the Collection page.
![]()
Select Host Metrics.
![]()
Enter a Name and an optional description. Then select the required items and click Save button.
![]()
Select Manage Data > Settings > Connections located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Click + button to add a new connection.
![]()
Select Webhook as Connection Type.
![]()
In the Create Webhook Connection dialog, enter a Name for the connection, an optional description. Then copy the URL created in AlertNow and paste it to URL field. Populate Payload field with the following content. Then, click Save button.
![]()
- Payload Sample
Metric
{
"alrtTypeCd": "metric",
"searchName": "{{SearchName}}",
"searchDescription": "{{SearchDescription}}",
"searchQuery": "{{SearchQuery}}",
"searchQueryUrl": "{{SearchQueryUrl}}",
"timeRange": "{{TimeRange}}",
"triggerTime": "{{FireTime}}",
"alertThreshold": "{{AlertThreshold}}",
"alertSource": "{{AlertSource}}",
"alertStatus": "{{AlertStatus}}",
"alertID": "{{AlertID}}"
}
Add Monitor
Select Manage Data > Alerts > Add Monitor located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Populate Query field and select the created one from list of Send Notification. Enter a Name for monitor and an optional description, and then click Save button.
![]()
The created monitor will be displayed in Alerts of Manage Data menu.
![]()
Set Up a Webhook Connection: Log
Sign in with Sumo Logic, and select Manage Data > Collection located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Select Add > Add Source in the Collection page.
![]()
Select Local File.
![]()
Fill in the required fields such as Name and File Path. Then click Save button.
![]()
Select + New > Log Search in the Collection page.
![]()
After entering a query in the Query field and click Save As.
![]()
Enter in a name and click on Schedule this search to specify the conditions.
![]()
Select an option from the Run Frequency menu. For Alert Type, select Webhook. Then select a connection from the Webhook connections list and click Save button.
![]()
- Payload Sample
Log
{
"alrtTypeCd": "log",
"searchName": "{{SearchName}}",
"searchDescription": "{{SearchDescription}}",
"searchQuery": "{{SearchQuery}}",
"searchQueryUrl": "{{SearchQueryUrl}}",
"timeRange": "{{TimeRange}}",
"triggerTime": "{{FireTime}}"
}
Nagios
To integrate Nagios with AlertNow, you must execute commands in the Nagios Core server.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Nagios card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Nagios Core Server
This guide describes how to install Nagios Core server; install via apt-get (Debian based, i.e. Ubuntu), yum (RHEL based, i.e. CentOS, Fedora), Linux package managers, and directly download Nagios Core source as well. Pick the right command for your IT environment. Please note that all commands must be executed as the root user.
On Nagios Core server, run commands sequentially as listed below.
1. Create the notify_service_alertnow.sh script
For installing the source directly, move to:
cd /usr/local/nagios/libexec
For Debian-based systems, move to:
cd /usr/lib/nagios/plugins
For RHEL-based systems, move to:
cd /usr/lib64/nagios/plugins
Create a shell script using the vi editor.
vi notify_service_alertnow.sh
Copy and paste the following code and add the URL created in AlertNow to <Enter AlertNow URL here>.
#!/bin/bash
ALERTNOW_URL=<Enter AlertNow URL here>
function notify_service_alertnow () {
curl -X POST ${ALERTNOW_URL} -H "Content-Type: application/json" -s -d "{\"alertType\": \"service\",\"notificationType\": \"$1\",\"serviceDesc\": \"$2\",\"serviceState\": \"$3\",\"hostName\": \"$4\",\"hostDisplayName\": \"$5\",\"serviceDisplayName\": \"$6\",\"serviceProblemId\": \"$7\",\"serviceOutput\": \"$8\",\"lastServiceProblemId\": \"$9\"}"
}
notify_service_alertnow "$1" "$2" "$3" "$4" "$5" "$6" "$7" "$8" "$9"
exit 0
Change the permission on the created script.
chmod +x notify_service_alertnow.sh
2. Create the notify_host_alertnow.sh script
For installing the source directly, move to:
cd /usr/local/nagios/libexec
For Debian-based systems, move to:
cd /usr/lib/nagios/plugins
For RHEL-based systems, move to:
cd /usr/lib64/nagios/plugins
Create a shell script using the vi editor.
vi notify_host_alertnow.sh
Copy and paste the following code and add the URL created in AlertNow to <Enter AlertNow URL here>.
#!/bin/bash
ALERTNOW_URL=<Enter AlertNow URL here>
function notify_host_alertnow () {
curl -X POST ${ALERTNOW_URL} -H "Content-Type: application/json" -s -d "{\"alertType\": \"host\",\"notificationType\": \"$1\",\"hostName\": \"$2\",\"hostState\": \"$3\",\"hostDisplayName\": \"$4\",\"hostProblemId\": \"$5\",\"lastHostProblemId\": \"$6\"}"
}
notify_host_alertnow "$1" "$2" "$3" "$4" "$5" "$6"
exit 0
Change the permission on the created script.
chmod +x notify_host_alertnow.sh
3. Create the alertnow.cfg file
For installing the source directly, move to:
cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects
For Debian-based systems, move to:
cd /etc/nagios3/conf.d
For RHEL-based systems, move to:
cd /etc/nagios/objects
Create a config file using the vi editor.
vi alertnow.cfg
Copy and paste the following code and save it.
define contact {
contact_name alertnow
alias AlertNow Contact
service_notification_period 24x7
host_notification_period 24x7
service_notification_options w,u,c,r
host_notification_options d,r
service_notification_commands notify-service-by-alertnow
host_notification_commands notify-host-by-alertnow
}
define command {
command_name notify-service-by-alertnow
command_line $USER1$/notify_service_alertnow.sh '$NOTIFICATIONTYPE$' '$SERVICEDESC$' '$SERVICESTATE$' '$HOSTNAME$' '$HOSTDISPLAYNAME$' '$SERVICEDISPLAYNAME$' '$SERVICEPROBLEMID$' '$SERVICEOUTPUT$' '$LASTSERVICEPROBLEMID$'
}
define command {
command_name notify-host-by-alertnow
command_line $USER1$/notify_host_alertnow.sh '$NOTIFICATIONTYPE$' '$HOSTNAME$' '$HOSTSTATE$' '$HOSTDISPLAYNAME$' '$HOSTPROBLEMID$' '$LASTHOSTPROBLEMID$'
}
4. Add the contact “alertnow” to contact.cfg file
For installing the source directly, move to /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects and open the config file in the vi editor.
cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects
vi contacts.cfg
For Debian-based systems, move to /etc/nagios3/conf.d and open the config file in the vi editor.
cd /etc/nagios3/conf.d
vi contacts_nagios2.cfg
For RHEL-based systems, move to /etc/nagios/objects and open the config file in the vi editor.
cd /etc/nagios/objects
vi contacts.cfg
Add the contact “alertnow” to members in the contactgroup and save it.
define contactgroup {
contactgroup_name admins
alias Nagios Administrators
members nagiosadmin,alertnow ; add alertnow here
}
5. Add the path to nagios.cfg file
For installing the source directly, move to /usr/local/nagios/etc and open the config file in the vi editor.
cd /usr/local/nagios/etc
vi nagios.cfg
Add the following path to the file and save it.
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/alertnow.cfg
For Debian-based systems, skip this step.
For RHEL-based systems, move to /etc/nagios and open the config file in the vi editor.
cd /etc/nagios
vi nagios.cfg
Add the following path to the file and save it.
cfg_file=/etc/nagios/objects/alertnow.cfg
6. Restart Nagios Core
Restart Nagios Core for your configuration changes to take effect.
For installing the source directly, execute any of the following commands.
===== Ubuntu 14.x =====
service nagios restart
===== Ubuntu 15.x / 16.x / 17.x / 18.x =====
systemctl restart nagios.service
===== RHEL 5/6 | CentOS 5/6 =====
service nagios restart
===== RHEL 7/8 | CentOS 7 =====
systemctl restart nagios.service
For Debian-based systems, execute the following command.
service nagios3 restart
For RHEL-based systems, execute the following command.
service nagios restart
Standard
AlertNow Standard allows you to send customized events and incident details to AlertNow. It allows you to manage events and incidents efficiently.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Standard card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Calling REST API
Call a REST API with the API Key created in AlertNow. Information required to call a REST API are:
About Standard Integration Call
URL: https://{DOMAIN}/integration/standard/v1/{APIKEY}
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/json
Body: Refers to the following tableMessage Spec
| Field | Name | Data Type | Mandatory | Description | Default Value | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| summary | Summary info | String | Required | Information that lets you identify the content of the event | Threshold Crossed: 1 datapoint [31.84234972677596 (19/12/19 17:40:00)] was greater than or equal to the threshold (90.0) | |
| event_id | Event ID | String | Optional | If event_id data does not exist, it will be automatically set (However, if status is ack or close, it is required) |
UUID | 129335065553 |
| status | Status info | String | Optional | Field indicating the status of the event Valid values: - open: event creation - ack: event confirmation - close: event end |
open | open |
| urgency | Urgency | String | Optional | Field indicating the degree of influence on system or the urgency of the event related to the priority Valid values: - highest - high - medium - low - lowest - none |
none | high |
| event_time | Occurred | String | Optional | Time at which an event occurred Timestamp (ISO 8601) data type |
Current timestamp | 2019-12-19T17:40:00+09:00 |
| metric_name | Metric name | String | Optional | Information that lets you identify a metric type | CPUUtilization | |
| threshold | Threshold | String | Optional | Metric threshold | 90 | |
| metric_value | Metric value | String | Optional | Measured value of metric | 93.1 | |
| resource_name | Resource name | String | Optional | Information that you can identify such as the host name of the system on which event occurred | i-9c09acd49a25 | |
| event_type | Event type | String | Optional | Information that lets you identify an event type | INFO | |
| custom_details | Details | JSON | Optional | More information field | { “ping time”: “1500ms”, “load avg”: 0.75 } |
- Payload Sample
{
"summary": "Threshold Crossed: 1 datapoint [31.84234972677596 (19/12/19 17:40:00)] was greater than or equal to the threshold (90.0)",
"event_id": "129335065553",
"status": "open",
"urgency": "high",
"event_time": "2019-12-19T17:40:00+09:00",
"metric_name": "CPUUtilization",
"threshold": "90",
"metric_value": "93.1",
"resource_name": "i-9c09acd49a25",
"event_type": "INFO",
"custom_details": {
"ping time": "1500ms",
"load avg": "0.75"
}
}
Kapacitor
To integrate Kapacitor with AlertNow, you need to write the TICKscript or create the Alert Rule Builder in Kapacitor.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Kapacitor card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Configuration on Kapacitor
- How to write the TICKscrip generating an alert when the memory metric exceed a threshold that you set
The steps below describe how to write the script to integrate Kapacitor with AlertNow. The script can be edited if required.
1. Write the alertnow_mem_alert.tick script
Move to the same directory as the kapacitor.conf file.
cd /etc/kapacitor
Write a script using the vi editor.
vi alertnow_mem_alert.tick
Copy and paste the following code and add the URL created in AlertNow to <Enter AlertNow URL here>.
Change each of the variable values and the ‘used_percent’ metric to values that you want to measure and then save them.
var alertnow_url = '<Enter AlertNow URL here>'
var measurement = 'mem'
var period = 10s
var every = 10s
var info = 80
var warn = 85
var crit = 90
var data = stream
|from()
.measurement(measurement)
|window()
.period(period)
.every(every)
var trigger = data
|alert()
.info(lambda: "used_percent" > info)
.warn(lambda: "used_percent" > warn)
.crit(lambda: "used_percent" > crit)
.stateChangesOnly()
.id('{{ .Name }}:used_percent')
.message(' {{.ID}} is {{.Level}}; value: {{ index .Fields "used_percent" }}')
.post(alertnow_url)
.skipSSLVerification()
2. Define the kapacitor task
Define the TICKscript written as kapacitor task.
// Pattern
kapacitor define <TASK_ID> -tick <PATH_TO_TICKSCRIPT> -dbrp <DATABASE>.<RETENTION_POLICY>
// Example
kapacitor define "alertnow_mem_alert" -tick /etc/kapacitor/alertnow_mem_alert.tick -dbrp telegraf.autogen
3. Enable the kapacitor task
Enable the kapacitor task.
// Pattern
kapacitor enable <TASK_ID>
// Example
kapacitor enable alertnow_mem_alert
4. Verify the kapacitor task
Verify the registered kapacitor task.
kapacitor list tasks
- Kapacitor is interworking with Chronograf
The steps below describe how to integrate Kapacitor with AlertNow when Kapacitor is connected with Chronograf.
From your Chronograph dashboard, in the left hand menu, select Alerting > Manage Tasks.
![]()
Click the Build Alert Rule button on the top right of the page.
![]()
Write the Alert Rule Builder sequentially as mentioned below.
① Enter the Alert Rule name.

② Select an Alert Type of the following options: Threshold, Relative and Deadman.

③ In the section Time Series, select a policy, a measurement & tag and a field to be monitored.

④ Define the Conditions for threshold.

⑤ In the section Alert Handlers, select the post and add the URL for the integration created in AlertNow to HTTP endpoint for POST request field.

⑥ Enter the Alert Message.

⑦ Click the Save Rule button in the top right corner.

SAMBA
Depending on your country or region, this feature may not be available.
To integrate SAMBA with AlertNow, you need to set the configuration as below.
Click Create integration button located on the top-left side, and select the SAMBA card.
![]()
- Enter an integration name and then configure the naming rules with the sample data.
![]()
- Sample data
{
"summary": "SAMBA > eu-idc > System > euidbmkaf04 > CPU Usage (SUM)",
"status": "open",
"urgency": "low",
"event_time": "2020-01-07T16:03:00+09:00",
"metric_name": "CPU Usage (SUM)",
"threshold": "90",
"metric_value": "93.1",
"resource_name": "SAMBA > eu-idc > System > euidbmkaf04",
"event_type": "INFO"
}
- Fill in the required information in the Service field and then click OK button to create integration.
![]()
Dynatrace
To integrate Dynatrace with AlertNow, you need to set Custom Webhook Integration in the Dynatrace.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Dynatrace card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Webhook Configuration
Sign in with Dynatrace, and click the menu button on the top left of the page.
![]()
Select Settings > Integration > Problem Notifications.
![]()
Click Set up notifications, and select Custom integration.
![]()
On the Set up custom integration screen, enter a Name for your integration, copy the URL for the integration in AlertNow and paste it to the Webhook URL field, populate Custom payload field with the following content.
![]()
- Payload Sample
{
"ImpactedEntities":{ImpactedEntities},
"ImpactedEntity":"{ImpactedEntity}",
"PID":"{PID}",
"ProblemDetailsHTML":"{ProblemDetailsHTML}",
"ProblemDetailsJSON":{ProblemDetailsJSON},
"ProblemDetailsMarkdown":"{ProblemDetailsMarkdown}",
"ProblemDetailsText":"{ProblemDetailsText}",
"ProblemID":"{ProblemID}",
"ProblemImpact":"{ProblemImpact}",
"ProblemSeverity":"{ProblemSeverity}",
"ProblemTitle":"{ProblemTitle}",
"ProblemURL":"{ProblemURL}",
"State":"{State}",
"Tags":"{Tags}"
}
- Click Send test notification. If everything goes well, you will receive a Custom integration test successful. Click Save to complete the configuration.
![]()
Elasticsearch Watcher
To integrate Elasticsearch Watcher with AlertNow, you need to configure Watcher in the Elasticsearch Watcher server.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Elasticsearch Watcher card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Configure in Elasticsearch Watcher
- Verify that Watcher is set up and running on your server:
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200/_watcher/stats?pretty'
You should get a response showing “watcher_state”: “started”:
{
"_nodes" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"manually_stopped" : false,
"stats" : [
{
"node_id" : "0lqYKcZuTV2AvspmQnLcmw",
"watcher_state" : "started",
"watch_count" : 1,
"execution_thread_pool" : {
"queue_size" : 0,
"max_size" : 10
}
}
]
}
- This example shows how to use a PUT request to register a new watch or update an existing watch. Replace the “trigger”, “input”, and “condition” with the ones you want to use to integrate Elasticsearch Watcher with AlertNow, and create the user-defined alerts. Add the URL created in AlertNow to <Enter AlertNow URL here>. The URL can be found in the AlertNow integration page.
curl -X PUT 'http://localhost:9200/_watcher/watch/alertnow_watch_01' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{
"trigger": {
"schedule" : { "interval" : "60s" }
},
"input": {
"search" : {
"request" : {
"indices" : [ "metricbeat*" ],
"body" : {
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"range": {
"system.process.cpu.total.pct": {
"gte": 50
}
}
},
"filter": {
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "now-60s"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
"condition": {
"compare" : { "ctx.payload.hits.total" : { "gte" : 1 }}
},
"actions": {
"alertnow": {
"webhook": {
"method":"POST",
"url":"<Enter AlertNow URL here>",
"headers":{
"Content-Type":"application/json"
},
"body": "{\"id\": \"{{ctx.id}}\",\"watchId\": \"{{ctx.watch_id}}\",\"triggeredTime\": \"{{ctx.trigger.triggered_time}}\",\"details\": {{#toJson}}ctx.payload{{/toJson}}}"
}
}
}
}'

- You can find detailed instructions on Configuring Watcher and Alerting in the Watcher Documentation.
- Confirm that the watch is registered or updated properly.
curl -X GET 'localhost:9200/.watches/_search?pretty'
📑 Note: Verify that an issue meets your watch’s condition and an alert is created.
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200/.watch_history*/_search?pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{
"query" : {
"match" : { "result.condition.met" : true }
}
}'
Depending on your country or region, this feature may not be available.
To integrate AlertNow with any service capable of sending email notifications, you need to set the configuration for the email you are using.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Email card.
![]()
Enter an integration name, email and then select the Suppression rules.
![]()
Fill in the required information in the Service field and then click OK button to create integration.
![]()
- Add the Integration Email to Your Monitoring Service
In order to complete the integration, refer to your monitoring service’s documentation on email integration, and then copy the integration email address and add it to your monitoring service.
AlertNow will create an incident when it receives an email from the email address you entered.
Scouter
To integrate Scouter with AlertNow, you need to download AlertNow Plugin and install it on the Scouter server.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Scouter card.
![]()
Enter an integration name and then define the naming rules.
![]()
Fill in the required information in the Service field and then click OK button to create integration.
![]()
Scouter Server
1. Install AlertNow Plugin
To integrate Scouter with AlertNow, install AlertNow Plugin.
Click Download AlertNow Plugin and save it to the subfolder lib/ of the Scouter server.
AlertNow Plugin
lib/scouter-plugin-server-alert-alertnow-1.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
2. Restart Scouter server
Add AlertNow Plugin setting values to the conf/scouter.conf file located in the subpath of Scouter server, and restart the server.
conf/scouter.conf
# External Interface (AlertNow)
ext_plugin_alertnow_send_alert=true
ext_plugin_alertnow_debug=true
ext_plugin_alertnow_level=0
ext_plugin_alertnow_webhook_url=<Enter AlertNow URL here.>
ext_plugin_alertnow_xlog_enabled=true
ext_plugin_elapsed_time_threshold=1500
ext_plugin_gc_time_threshold=1000
ext_plugin_thread_count_threshold=1000
- Notification setting options
① ext_plugin_alertnow_send_alert: Whether to send AlertNow message (true/false) - Default is false
② ext_plugin_alertnow_debug: Whether to log - Default is false
③ ext_plugin_alertnow_level: Alert level (0: INFO, 1: WARN, 2: ERROR, 3: FATAL) - Default is false
④ ext_plugin_alertnow_webhook_url: Enter AlertNow Webhook URL
⑤ ext_plugin_elapsed_time_threshold: Response time threshold (ms) - Default is 0, the response time threshold is not be checked when it is 0
⑥ ext_plugin_gc_time_threshold: GGC Time threshold (ms) - Default is 0, the GC Time threshold is not be checked when it is 0
⑦ ext_plugin_thread_count_threshold: Thread Count threshold - Default is 0, the Thread Count threshold is not be checked when it is 0
⑧ ext_plugin_alertnow_xlog_enabled: Send xlog message (true/false) - Default is false
The following alerts are currently supported:
- Connect new Agent
- Disconnect Agent
- Reconnect Agent
- Elapsed Time threshold exceeded
- GC Time threshold exceeded
- Thread Count threshold exceeded
3. Set up Host Agent notification
Add the setting value to the conf/scouter.conf file located in the subpath of the host agent when you want to notify about the data collected by the host agent and exceed the threshold. Only CPU, Memory and Disk notifications can be set.
conf/scouter.conf
### scouter host configuration
cpu_alert_enabled=true
cpu_warning_pct=90
cpu_fatal_pct=95
cpu_check_period_ms=60000
cpu_fatal_history=3
cpu_alert_interval_ms=300000
mem_alert_enabled=true
mem_alert_interval_ms=120000
mem_warning_pct=80
mem_fatal_pct=90
disk_alert_enabled=true
disk_warning_pct=70
disk_fatal_pct=90
CPU notification setting options
① cpu_alert_enabled: Enable or Disable cpu notification (Default: true)
② cpu_warning_pct: Percent of cpu warning level notification (Set to integer)
③ cpu_fatal_pct: Percent of cpu fatal level notification (Set to integer)
④ cpu_check_period_ms: Specify the period for checking cpu
⑤ cpu_warning_history, cpu_fatal_history: Specifies how many times the setting value of each level is exceeded to send notification (e.g. if cpu_fatal_pct is 90%, cpu_check_period_ms is 5 minutes (300000ms), and cpu_fatal_history is 3, notification will be sent when the CPU is 90% for the last 5 minutes)
⑥ cpu_alert_interval_ms: Do not send the same notification for time interval you setMemory notification setting options
① mem_alert_enabled=true
② mem_alert_interval_ms=30000
③ mem_warning_pct=80
④ mem_fatal_pct=90Disk usage notification setting options
① disk_alert_enabled=true
② disk_warning_pct=70
③ disk_fatal_pct=90
4. Set up Customized notification
Select the metric you want to generate a notification from Scouter Client UI.
Write a custom notification script in JAVA language and save it as shown below.
Alert Script in the top left of the screen is the area for writing scripts, and API Help in the top right of the screen is the help screen for the two parameters $counter and $$ passed to the script. Alert Configuration at the bottom left of the screen is to configure an alert verification cycle, and Console Output at the bottom right is a console window that informs whether the code compiles successfully when the notification script is saved.
- Alert Configuration
① history_size=150
Scouter counter value is collected every 2 seconds. In other words, 150 means to keep up to 150 values of the recent data and data values in the past 300 seconds.
This information is used to compare with old data when writing the notification script.
② slient_time=300
This is the snooze time and this value is specified in seconds. If a notification is sent, it will not be sent for 300 seconds when the value is set.
③ check_time=2
This value is specified in seconds. Setting it to 2 runs the above notification script every 2 seconds. You can adjust it according to the value you want to measure.
Alert script files are editable directly on the Scouter server. For details, see Scripting in Scouter Server.
Amazon GuardDuty
To integrate Amazon GuardDuty with AlertNow, you need to set a topic, subscription and event rule in the AWS Console.
- Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Amazon GuardDuty card.

- In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.

Access AWS Console
To connect AWS GuardDuty with AlertNow, you need to create a SNS topic in the AWS Console.
From the AWS Console, type SNS in the search field, and then select Simple Notification Service.

Create SNS Topic and Subscription
On the Amazon SNS dashboard, select Topics.
1. Create New Topic
Select Create topic located on the top-right of the screen. The Create topic screen will appear.

The table below provides descriptions for each item. Click Create topic button.
| Item | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Topic Name | It is a communication channel to send messages and subscribe notifications and used to create an ARN for later created Topics. |
|
| Maximum 256 characters. Can include alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-) and underscores (_). | Required | |
| - For example, CreateSNSTopicTest: ‘arn:aws:sns:us-west-2:111122223333:CreateSNSTopicTest’ | ||
| Display Name | It is the name displayed for your topic when subscribing to SNS. | Optional |
Click Create topic button.
2. Create Subscription as shown
Select Create subscription located on the top-right of the screen.

The Create subscription screen will appear. Click Create Subscription button.

The table below provides descriptions for each item.
| Item | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Topic ARN | It is automatically reflected based on the created Topic Name. | Editable |
| Protocol | Select HTTPS. | |
| Endpoint | Paste the URL for the integration created in AlertNow. | Required |
3. Confirm Subscription
The subscription is being created.

Click Request confirmation button on at the upper right. Approval confirmation is made for the Subscription ID.

Create CloudWatch Event Rule
In the AWS management console, enter ‘CloudWatch’ in the search field to go to the CloudWatch console. Select Events, Create rule at the left side of the screen and then click Create rule.
Step 1: Select GuardDuty for the service name and GuardDuty finding for the event type.
For Targets, select SNS topic, and then click Configure details.

Step 2: Enter a name for the event rule and then click Create rule.

The rule has been created.

GuardDuty Sample findings
In the AWS console, enter ‘GuardDuty’ in the search field to go to GuardDuty console.
Select Settings at the left side of the screen and click Generate sample findings.

The sample findings will be displayed in the Findings menu.

Consul
To integrate Consul with AlertNow, you need to set the Consul Server.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Consul card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Copy the Integration URL for your new integration.
![]()
Consul Server
Refer to Consul-Alerts guide for installation.
(Version v0.6.0 or later of Consul health checks based Simple Daemon for sending notifications needs to be installed)Run Consul-Alerts.
nohup consul-alerts start --watch-checks --log-level=info &
- Once Consul-Alerts is running, you can configure HTTP Endpoint built-in notifier using curl.
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled | Enable the http-endpoint notifier (Default: false) |
| cluster-name | The name of the cluster (Default: “Consul Alerts”) |
| base-url | Base URL of the HTTP endpoint (Mandatory) |
| endpoint | The endpoint to append to the end of base-url |
| payload | The payload to send to the HTTP endpoint (Mandatory) |
① Base URL Configuration
Configure the base-url by adding the URL created in AlertNow to {Enter AlertNow URL here}.
curl -X PUT -d '{Enter AlertNow URL here.}' http://localhost:8500/v1/kv/consul-alerts/config/notifiers/http-endpoint/base-url
② Payload Configuration
curl -X PUT 'http://localhost:8500/v1/kv/consul-alerts/config/notifiers/http-endpoint/payload' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{
"node":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Node}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"serviceId":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.ServiceId}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"service":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Service}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"checkId":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.CheckId}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"check":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Check}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"status":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Status}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"output":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Output}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"notes":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Notes}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"interval":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Interval}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"rmdCheck":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.RmdCheck}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"notifList":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.NotifList}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"varOverrides":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.VarOverrides}}{{end}}{{end}}",
"timestamp":"{{range $name, $checks := .Nodes}}{{range $check := $checks}}{{$check.Timestamp}}{{end}}{{end}}"
}'
③ Enable AlertNow notifications in Consul-Alerts
To enable this, set consul-alerts/config/notifiers/http-endpoint/enabled to true.
curl -X PUT -d 'true' http://localhost:8500/v1/kv/consul-alerts/config/notifiers/http-endpoint/enabled
④ Verify the settings
When setup is complete, you can see this in Key/Value Store.

Consul-Alerts will open the alert once health checks are critical.
![]()
Consul-Alerts will resolve the alert once health checks are passing.
![]()
Jennifer4
To integrate Jennifer4 with AlertNow, you need to configure Adapter in the Jennifer Server.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Jennifer4 card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Copy the Integration URL for your new integration.
![]()
Download Jennifer4 Adapter for AlertNow
To integrate Jennifer, click Download Jennifer Adapter for AlertNow to download. Jennifer4 is not compatible with Jennifer5 version.
- JDK versions available for integration with AlertNow
① jdk 1.5: Not available
② jdk 1.6: Not available
③ jdk 1.7: Available (7 ~ 7u80, including OpenJDK)
④ jdk 1.8: Available (8 ~ 8u241, including OpenJDK)
*Jennifer4 supports JDK 1.5 to 1.8, but you must be using JDK 1.7 or later to integrate with AlertNow.
Configure Adapter
Shutdown the running Jennifer Server by executing shutdown.sh in the /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/bin directory.
Open AlertNowNotiAdapter.java file using the vi Editor or Document Editor. The file must be saved in UTF-8 encoding. Changing the encoding might cause compile failure.
Paste the URL for the integration created in AlertNow to within double quotes in the private static final String ALERTNOW_JENNIFER_INTEGRATION_URL as shown below.
📑 Note: Do not modify any information except Webhook URL. If other information is changed, the integration with AlertNow may not work properly.

Move the modified file to /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/common/lib directory.
![]()
Ensure that jenniferserver.jar file exists in /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/common/lib directory. If it does not exist, please contact your Server administrator or Jennifer Support.
If the file exists in /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/common/lib directory, move AlertNowNotiAdapter.java file in the directory and use the following commands to compile them.
① javac -d . -cp ./jenniferserver.jar AlertNowNotiAdapter.java
② jar uvf jenniferserver.jar ./com
If you are running the java command, com directory is created at /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/common/lib and the class file for AlertNowNotiAdapter.java is located in the directory.
![]()
When the class file is created after running the java command, use the jar uvf command to merge/compile source code.
![]()
After merging AlertNowNotiAdapter.java file, move to /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/bin directory. Modify jennifer.properties file using the vi Editor or Document Editor as shown below.
sms_adapter_class_name = com.javaservice.jennifer.server.AlertNowNotiAdapter
The sms_adapter_class_name exists in both Auto-notification and Customize. Only the one should be activated and modified. If not, both will not work.
Run startup.sh in the /{Jennifer4 Server Home}/bin directory to start Jennifer4 server. To integrate alerts from Jennifer4 with AlertNowNotiAdapter, configure alert and SMS settings as below. When the TOT and Agent IDs are displayed in the Type for Alert Management in Properties, click the IDs to set the alerts. Select the alert list and move it to the right side, and then select Enable Alert and Enable SMS check boxes.
- SMS is the only external interface of Jennifer4 and it is configured with AlertNow Adapter. Thus, you should select Enable SMS to integrate with AlertNow.
- If Enable Alert and Enable SMS are not enabled, the alert list can only be seen in the Web Monitoring and it does not integrate with the external service.
![]()
- See the Log for Adapter at / {Jennifer4 Server Home}logs/catalina.out.
![]()
WhaTap
To integrate WhaTap with AlertNow, you need to configure a webhook in the WhaTap Server.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the WhaTap card.
![]()
Create integration screen will be displayed as below. Enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Webhook Configuration
Sign in with WhaTap, and select a project in the project list.
![]()
Select Alert > Alert Reception CONF. located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Click Add button from the 3rd Party Plugin.
![]()
Select the AlertNow tap and enter a channel name. Then copy the URL for the integration created in AlertNow and paste it to Webhook URL field, and then click Add button.
![]()
Select Alert > Alert CONF. located on the left side of the screen.
![]()
Set the alert policy, and then click Save button to complete the configuration.
![]()
Zenius
To integrate Zenius with AlertNow, you need to set notifications and surveillance in the Zenius console.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Zenius card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Notification Settings
Sign in to Zenius with a Super account.
![]()
Select Operation > Environment Settings > Notification from the Zenius dashboard.
AlertNow is already registered, and the default is set to Not active. Change it to Activate. After changing it to Activate, register AlertNow by selecting Register from the notification settings.
![]()
- In the Notification Settings window, select AlertNow as type. Enter required information and click OK button.
- Description: Enter a name and description (e.g.: AlertNow integration)
- Host & Port: Enter host address and port number to access (https://alertnowitgr.opsnow.com,443)
- URL: Enter the Integration URL created in AlertNow (integration/zenius/v1/b32a7d2835c65111eb1b97b70a8d4ec9fa9c)
![]()
- In the Set Time Zone, the settings popup window opens when you click a date.
- Notification Method: Select the checkbox of AlertNow to Activate Notification and unselect the checkbox to Deactivate Notification
- Time: Notify at times you set in Time 1 and Time 2
![]()
Surveillance Settings
Sign in to the Zenius with Admin account.
![]()
Select SMS > Settings > Surveillance Settings from the Zenius dashboard.
Click Register & Modify button to open Registering Surveillance Settings windows.
![]()
In Registering Surveillance Settings window, set events to surveil, server, time/date, and notification method. Select AlertNow for notification method, and choose Notify when returns to normal as a notification option.
![]()
When AlertNow is displayed as the notification method, the settings is successfully configured.
![]()
When you sign in with Admin account, you can check the history of notifications sent to AlertNow from Operations > Logs > AlertNow sent menu.
Zabbix
To integrate Zabbix with AlertNow, you need to configure Media types and Actions in the Zabbix console.
Click Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Zabbix card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click the OK button to create the integration.
![]()
This guide explains how to send event notifications by using Custom Alertscripts and Webhook.
Using Custom Alertscript
You can use all Zabbix versions that support the Custom Alertscript feature. Details of this guide are based on Zabbix version 4.2.
1. Write Alert script (execute in root permission)
① Open ‘zabbix_server.conf’ file in the vi editor and check the AlertScriptsPath.

② Under /usr/lib/zabbix/alertscripts, write notify_to_alertnow.sh script and then save. The path may be different depending on your OS.
#!/bin/bash
sendto=$1
subject=$2
message=$3
alertnow_url=$4
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{\"subject\":\"$subject\", \"message\":$message}" $alertnow_url
③ Modify the owner of notify_to_alertnow.sh and its mode as following:
2. Create Media Type
① To add Macros, go to Administration > General and select Macros. Click [Add] button, and insert {$ZABBIX.URL} in Macro field and the Zabbix URL in the Value field and click the [Update] button.

② To create Media type, go to Administration > Media types, click the [Create Media type] button on the upper-right corner.

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter AlertNow in the Name field. |
| Type | Select Script in the Type field. |
| Script name | Enter ‘notify_to_alertnow.sh’ in the Script name field. |
| Script parameters | Enter the following in order. {ALERT.SENDTO} {ALERT.SUBJECT} {ALERT.MESSAGE} (Enter the AlertNow URL here) - Enter the actual AlertNow URL here. |
③ Click the [Add] button to save, and click the [Test] button in the newly created AlertNow Media Type and fill in the following on the modal pop-up window.

④ Click the [Test] button to see if the notification is working properly.

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Send to | Enter AlertNow in the Send to the field. |
| Subject | Enter Test subject in the Subject field. |
| Message | Enter { “eventName”: “This is the test message from Zabbix”, “eventId”: “testId01” } in the Message field, and enter different eventId values for each test. |
3. Create Users
① Under Administration > Users menu, click the [Create user] button on the upper-right corner. Enter the following in the User tab menu.

② Click Media tab and Click the [Add] button.

③ Enter each item on the popup window. When active sets the date and time period when you will be receiving notifications, and Use if severity lets you select severity levels of notifications that you want to be notified of.

④ Click the Permission tab menu to see if you have Read permission or higher. To create a User, click the [Add] button to save.

⑤ If proper permissions are not granted, go to the added User groups and grant the permission of Read or higher for Host group’s permissions under the Permissions tab.

4. Create Actions
① Under Configuration > Actions menu, click the [Create action] button on your upper-right corner. Enter AlertNow Action in the Name field in the Action tab menu.

② Enter each item in the Operations tab, and click the [Add] button to save.

📑 Note: In the case of a default message, you must enter them according to the given JSON standard.
③ If there is a Macro that is not supported by Zabbix’s previous versions, use {EVENT.NAME} → {TRIGGER.NAME}, {EVENT.SEVERITY} → {TRIGGER.SEVERITY} instead.
- Default message
{
"eventDt": "Problem started at {EVENT.TIME} on {EVENT.DATE}",
"eventName": "{EVENT.NAME}",
"host": "{HOST.NAME}",
"severity": "{EVENT.SEVERITY}",
"eventId": "{EVENT.ID}",
"eventStatus": "open",
"triggerUrl": "{$ZABBIX.URL}/tr_events.php?triggerid={TRIGGER.ID}&eventid={EVENT.ID}"
}
④ Enter each item in the Recovery operations tab, and click the [Add] button to add Operation details.
📑 Note: In the case of a default message, you must enter them according to the given JSON standard.

- Default message
⑤ To create Actions, click the [Add] button to save.
5. Check Incident Creation in AlertNow
Modify Trigger configuration in Zabbix and directly create a test event and see if incidents were properly created in AlertNow by checking SMS, email, Voice Call, or Slack notifications.
Using Webhook
You can use all Zabbix versions 4.4 or higher that support the Webhook feature. Details of this guide are based on the Zabbix 5.0 LTS version.
1. Create Media type
① To create Macros, go to Administration > General menu, and select Macros from the upper-left select box. Click the [Add] button and insert {$ZABBIX.URL} in the Macro field and the Zabbix URL in the Value field and click the [Update] button.

② To select Media type, go to Administration > Media types menu, and click the [Create media type] button on the upper-right corner.

③ Enter AlertNow in the Name field, and select Webhook in Type. Then, enter the following in order in the Name and Value fields.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| alertnow_url | Enter the actual AlertNow URL here |
| alert_message | {ALERT.MESSAGE} |
| alert_subject | {ALERT.SUBJECT} |
| event_date | {EVENT.DATE} |
| event_id | {EVENT.ID} |
| event_name | {EVENT.NAME} |
| event_nseverity | {EVENT.NSEVERITY} |
| event_severity | {EVENT.SEVERITY} |
| event_source | {EVENT.SOURCE} |
| event_time | {EVENT.TIME} |
| event_update_status | {EVENT.UPDATE.STATUS} |
| event_value | {EVENT.VALUE} |
| host_name | {HOST.NAME} |
| trigger_id | {TRIGGER.ID} |
| zabbix_url | {$ZABBIX.URL} |
④ Click the pencil icon to modify Script, and enter javascript as below and then save.
AlertNow Javascript
var AN = {
payload: {},
validateParams: function (params) {
if (isNaN(params.event_id) || params.event_id < 1) {
throw 'Field "event_id" is not a positive number';
}
if (params.alert_subject.length < 1) {
throw 'incorrect value for variable "alert_subject". The value must be a non-empty string.';
}
if ([0, 1, 2, 3].indexOf(parseInt(params.event_source)) === -1) {
// 0 - Trigger, 1 - Discovery, 2 - Autoregistration, 3 - Internal
throw 'Incorrect "event_source" parameter given: "' + params.event_source + '".\nMust be 0-3.';
}
if (params.event_source !== '0') {
params.event_nseverity = '0';
params.event_severity = 'Not classified';
params.event_update_status = '0';
}
if (params.event_source === '1' || params.event_source === '2') {
params.event_value = '1';
}
if ([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5].indexOf(parseInt(params.event_nseverity)) === -1) {
// 0 - Not classified, 1 - Information, 2 - Warning, 3 - Average, 4 - High, 5 - Disaster
throw 'Incorrect "event_nseverity" parameter given: ' + params.event_nseverity + '\nMust be 0-5.';
}
if (typeof params.event_severity !== 'string' || params.event_severity.trim() === '') {
throw 'Field "event_severity" cannot be empty';
}
if (params.event_update_status !== '0' && params.event_update_status !== '1') {
// 0 - Webhook was called because of problem/recovery event, 1 - Update operation
throw 'Incorrect "event_update_status" parameter given: ' + params.event_update_status + '\nMust be 0 or 1.';
}
if (params.event_value !== '0' && params.event_value !== '1') {
// 1 for problem, 0 for recovering
throw 'Incorrect "event_value" parameter given: ' + params.event_value + '\nMust be 0 or 1.';
}
if (typeof params.host_name !== 'string' || params.host_name.trim() === '') {
throw 'Field "host_name" cannot be empty';
}
if (isNaN(params.trigger_id) && params.event_source === '0') {
throw 'field "trigger_id" is not a number';
}
if (typeof params.zabbix_url !== 'string' || params.zabbix_url.trim() === '') {
throw 'Field "zabbix_url" cannot be empty';
}
if (!/^(http|https):\/\/.+/.test(params.zabbix_url)) {
throw 'Field "zabbix_url" must contain a schema';
}
},
buildPayload: function (params) {
AN.payload.subject = params.alert_subject;
var dtPrefix = '';
switch (params.event_source) {
case '0':
if (params.event_update_status === '0') {
if (params.event_value === '1') {
dtPrefix = 'Problem started at ';
AN.payload.message = {
'eventDt': dtPrefix + params.event_time + ' on ' + params.event_date,
'eventName': params.event_name,
'host': params.host_name,
'severity': params.event_severity,
'nseverity': params.event_nseverity,
'eventId': params.event_id,
'eventStatus': 'open',
'triggerUrl': params.zabbix_url + '/tr_events.php?triggerid=' + params.trigger_id + '&eventid=' + params.event_id
};
} else {
AN.payload.message = {
'eventId': params.event_id,
'eventStatus': 'close'
};
}
}
break;
case '1':
dtPrefix = 'Discovery: at ';
AN.payload.message = {
'eventDt': dtPrefix + params.event_time + ' on ' + params.event_date,
'eventId': String(new Date().getTime()),
'eventStatus': 'open'
};
AN.payload.detail = params.alert_message;
break;
case '2':
dtPrefix = 'Autoregistration: at ';
AN.payload.message = {
'eventDt': dtPrefix + params.event_time + ' on ' + params.event_date,
'eventId': String(new Date().getTime()),
'eventStatus': 'open'
};
AN.payload.detail = params.alert_message;
break;
case '3':
dtPrefix = 'Internal problem started at ';
AN.payload.message = {
'eventDt': dtPrefix + params.event_time + ' on ' + params.event_date,
'eventId': String(new Date().getTime()),
'eventStatus': 'open'
};
AN.payload.detail = params.alert_message;
break;
}
},
request: function (url) {
var req = new CurlHttpRequest();
req.AddHeader('Content-Type: application/json');
if (typeof AN.payload.HTTPProxy === 'string' && AN.payload.HTTPProxy.trim() !== '') {
req.SetProxy(AN.payload.HTTPProxy);
}
req.Post(url, JSON.stringify(AN.payload));
return req.Status();
}
}
try {
Zabbix.Log(4, 'AlertNow notification value : ' + value);
var params = JSON.parse(value);
if (params.event_source === '0' && params.event_update_status === '1') {
throw 'Update operation is not called through webhook.';
}
AN.validateParams(params);
var result = {tags: {}},
resp = {};
AN.buildPayload(params);
resp = AN.request(params.alertnow_url);
if (resp !== 200) {
throw 'Response code: ' + resp;
}
result.tags.endpoint = 'AlertNow';
} catch (error) {
Zabbix.Log(3, '[ AlertNow Webhook ] AlertNow notification failed payload : ' + JSON.stringify(AN.payload));
Zabbix.Log(3, 'AlertNow notification failed : ' + error);
result = {};
}
return JSON.stringify(result);
⑤ Go to the Message templates tab, and click the [Add] button.

⑥ Select Problem, Problem recovery, Discovery, and Autoregistration for each of Message types from the popup window to register a total of four Message templates. Click the [Add] button to save.

➆ Click the [Add] button of the Media type to save.
2. Create User
① Under Administration > Users menu, click the [Create User] button on the upper-right side. Enter each item under the User tab.

② Select the Media tab, and click the [Add] button.

③ Enter each item on the popup window. ‘When active’ sets the date and time period when you will be receiving notifications, and ‘Use if severity’ lets you select severity level notifications that you want to be notified of.

④ Click the Permission tab to see if you have Read permission or higher. To create a User, click the [Add] to save.

⑤ If proper permissions are not granted, go to the added User groups and grant permissions of Read or higher for Host group’s permissions under the Permissions tab.
3. Create Actions
① Under Configuration > Actions menu, click the [Create action] button on your upper-right corner. Enter AlertNow Action in the Name field under the Action tab.

② Enter each item of Operations and Recovery operations in the Operations tab in the modal popup window. Click the [Add] button to save.

③ Select AlertNow User in the Send to field and select AlertNow in the Send only to field. Click the Add button to save and to create AlertNow Actions. Finally, click the Add button to save.

4. Check Incident Creation in AlertNow
Modify the Trigger configuration in Zabbix and directly create a test event, and see if incidents were properly created in AlertNow by checking SMS, email, Voice Call, or Slack message notifications.
Cloud Insight
To integrate Cloud Insight with AlertNow, you need to set Event Rules in the Cloud Insight console.
Click the Create Integration button located on the top-left side, and select the Cloud Insight card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click the OK button to create the integration.

Event Rules Settings
📑 Note: Refer to Cloud Insight User Guide for detailed instructions on how to collect various performance indicators of monitoring targets and set thresholds via Cloud Insight.
Go to Configuration > Event Rule of Cloud Insight, and click Create Event Rule button.
![]()
Choose monitoring product and click Next button.
![]()
Choose a monitoring target. If there is not monitoring target, click Create Group and select the target.
![]()
Set monitoring items and conditions. If there is no monitoring item, click Create Template and select the items.
![]()
Set actions to be executed when an event occurs. Click Create Channel button from the Integration tab, and create a channel using the AlertNow URL.
![]()
![]()
Enter a rule name and click Create button.
![]()
AWS Personal Health Dashboard
To connect AWS Personal Health Dashboard with AlertNow, you need to create an SNS topic, subscription, and event rule.
Click Create Integration button on the top-left corner of the Integration page, and select AWS Personal Health Dashboard card.
![]()
In the Create Integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button.
![]()
Access AWS Console
To connect AWS Personal Health Dashboard with AlertNow, you need to sign in to Amazon Console first. From the console, type SNS, and then select Simple Notification Service.

Create Amazon SNS Topic and Subscription
Select Topics in the Amazon SNS dashboard.
1. Create New Topic
Select Create topic on the top-right corner of the screen.

The Create topic screen will appear for you to enter required information.

The table below provides descriptions for each item.
| Item | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Topic Name | The name of the topic you want to create, and is the communication channel to send messages and subscription notifications and used to create an ARN for SNS topics that are created later. Topic names must include only uppercase and lowercase ASCII letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens, and must be between 1 and 256 characters long. |
Required |
* For example, create with the name of TestCaseForSNSTopic,arn:aws:sns:us-west-2:111122223333:TestCaseForSNSTopic |
||
| Display Name | The display name to use for an Amazon SNS topic with SMS subscriptions. | Optional |
2. Create Subscription
Select Create subscription on the top-right corner of the screen.

Fill in the required input fields in the Create subscription page, and click Create subscription button.

The table below provides descriptions for each item.
| Item | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Topic ARN | It is automatically applied based on the topic name created. | Can be edited |
| Protocol | Select HTTPS. | |
| Endpoint | Enter the URL for the integration created in AlertNow. | Required |
3. Confirm Subscription
The subscription will be created as shown below.

Click Request confirmation button, and then Subscription ID will be confirmed.

Create CloudWatch Event Rule
Go to CloudWatch console and select events and rules in sequence, and click Create rule.
Select Health for the service name and choose an event type you want to use. For Targets, select SNS topic, and click Configure details. For event type, you may have options for Any… or Specific…. You can create a rule by selecting a pattern or custom-generated event.
![]()
Enter a name for the event rule and then click Create rule.
![]()
Tencent Cloud Monitor
To integrate Tencent Cloud Monitor with AlertNow, you need to set the Notification Template from Tencent Cloud Monitor.
Click Create Integration button on the top-left corner of the page, and select the Tencent Cloud Monitor card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Access Tencent Cloud Console
Sign in to the Tencent console.
![]()
From the Tencent console, select Product -> Developer Service -> Cloud Monitoring in sequence.
![]()
Refer to User Guide for gathering performance metrics about monitoring targets and set threshold values by Tencent Cloud Monitor.
Notification Template Settings
Go to Notification Template of Cloud Monitoring and click Create button.
![]()
Fill in the required input fields and enter AlertNow URL created in the Create integration step.
![]()
In the Alert Strategy menu on the left side of the Cloud Monitoring page, you can set up alert-related rules such as setting conditions that trigger notifications and adding recipients.
![]()
CheckMK
To integrate CheckMK with AlertNow, you need to add CheckMK plugin.
Click Create Integration button on the top-left corner of the page, and select the CheckMK card.
![]()
In the Create integration page, enter the required information and then click OK button to create the integration.
![]()
Add CheckMK Plugin
- Get the script below after installing the CheckMK plugin.
#!/usr/bin/python
# AlertNow
import json
import os
import requests
def main():
context = dict([(var[7:], value.decode("utf-8"))
for (var, value) in os.environ.items()
if var.startswith("NOTIFY_")])
if context['NOTIFICATIONTYPE']=='PROBLEM' or context['NOTIFICATIONTYPE']=='RECOVERY' or context['NOTIFICATIONTYPE']=='ACKNOWLEDGEMENT':
print('NOTIFICATIONTYPE ' + context['NOTIFICATIONTYPE'] + ' supported')
else:
print('NOTIFICATIONTYPE ' + context['NOTIFICATIONTYPE'] + ' not supported')
return "NOTIFICATIONTYPE " + context['NOTIFICATIONTYPE'] + " not supported"
for k, v in context.items():
if (v.startswith('$') and v.endswith('$')):
context[k]=''
if "PARAMETER_1" in context:
alertnow_url = context["PARAMETER_1"]
if "PARAMETER_1" in context.keys():
del context["PARAMETER_1"]
if "PARAMETERS" in context.keys():
del context["PARAMETERS"]
else:
print('no API key Specified')
return "No API Key Specified."
url = alertnow_url
headers = {'Content-Type' : 'application/json'}
print(context)
try:
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(context, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=False))
print(response.text)
is_success = True
except:
is_success = False
if is_success:
print('Script Success')
return "Script finished successfully."
else:
print('Script Failed')
return "Script failed."
main()- Put the script under the directory below, and give the necessary permissions to the script using the command below.
/omd/sites/{site-name}/local/share/check_mk/notifications/
Permission command
sudo chmod +x alertnow
Configuration in CheckMK
- In CheckMK, click Setup > Users > Add user.
- Enter a Username and Full name.
- Leave the Authentication part blank.
- Check Disable password, and select Normal monitoring user for Roles.
- Click Save.

Click on the notification button under Actions column.
![]()
Click Add rule.
![]()
If the CheckMK plugin is properly installed, you can select AlertNow from the Notification Method.
![]()
Select AlertNow as the Notification Method and choose Call with the following parameters. Paste the AlertNow URL into the first parameter box.
![]()
Go back to the user list, and click Changes. Click Activate on selected sites to save the changes. Now your CheckMK integration is configured.
![]()
![]()
Note
If Checkmk alerts are triggered but AlertNow fails to create incidents, check the notification logs about potential errors in
/omd/sites/{site-name}/var/log/notify.logor request for help.AlertNow displays messages like
PROBLEM,ACKNOWLEDGEMENT, andRECOVERY, but notFLAPPINGSTART,DOWNTIMESTART, or etc.If
HOSTchanges intoDOWN→UPorSERVICEchanges intoOK, send theRECOVERYmessage and the incident will be closed automatically.If you encounter
Python ImportError: No module named requestserror, install theRequestsmodule to solve the issue as below.
![]()
$sudo apt install python-pip
$sudo pip install requests
Extensions
Extension allows you to export AlertNow incident-related notifications to external channels or services. AlertNow currently supports Slack, JANDI, and Generic Webhook, and other services will be added soon.
Slack
Add Slack
Click Extensions menu.
![]()
Click Add Extension button.
![]()
Enter the required information below.
![]()
The table below provides descriptions of each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter an extension name. |
| Extension type | Select an extension type. Default is set to Slack. |
| Service | Select a service to be added in the integration. |
| Notification event | Select events to receive incident notifications. |
| Language | Select a language to receive notifications. |
| Notification target | Specify users who can acknowledge or close incidents. Default is set to “AlertNow user only”. |
Click OK button.
In Slack channel authorization page, select a channel to post to, and click Allow button.
![]()
Extension is added to the service you selected.
📑 A single AlertNow account can be added to a WorkSpace. If another AlertNow account has been mapped to the WorkSpace, you cannot add a new account. To add your account with the mapped WorkSpace, set Run Command as Not Use. However, you cannot run Slack commands, but only receive notifications.
Slack Commands
Users can create, acknowledge, close, or assign incidents within Slack entering commands. Message is updated according to actions taken. The result of the action is posted to the designated channel.
- Run Command Option
To run the command, under the Extension settings, choose Run Command and select Use as shown below.

- Available Slash Commands
Available commands for AlertNow:
/an help: Display help message for the command.
/an create: Create a new incident manually.
/an ack [incidentID incidentID2..]: Change the incident status to Acknowledged.
/an close [incidentID incidentID2..]: Change the incident status to Closed.
/an assign [incidentID incidentID2..] to [userID:email]: Assign the incident.
/an list: View a list of incidents that were created in the service.
Generic Webhook
Add Generic Webhook
Click Extensions menu.
![]()
Click Add Extension button.
![]()
Enter the required information below.
![]()
The table below provides descriptions of each item.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter an extension name. |
| Extension type | Select an extension type. Default is set to Generic Webhook. |
| Service | Select a service to be added in the integration. |
| Notification event | Select events to receive incident notifications. |
| URL | Enter your endpoint URL. |
| URL Encode | Choose whether to use URL Encode when you add a General Webhook. |
| Method | Select a method from POST, PUT, DELETE or GET. |
| Custom Header | To add a Custom Header to your webhook, select [+ Add]. |
| Payload | Configure a payload. |
- Click OK button, and then you can see the added extension.
JANDI
Add Incoming Webhook
Click [Extension].
![]()
Click [Add Extension] button.
![]()
Copy the Webhook URL that was created in Incoming Webhook of JANDI Connect, and paste it into the URL field in the Create Extension page.
![]()
Enter the required information below.
![]()
The table below provides descriptions of each item.
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Enter an extension name. | |
| Extension type | Select an extension type. Default is set to JANDI. | |
| Service | Select a service to be added in the integration. | |
| Notification event | Select events to receive incident notifications. | |
| Language | Select a language to receive notifications. | |
| URL | Enter a Webhook URL created in the JANDI Connect. |
- Click [OK] button, and then you can see the added extension to the service.
Add Outgoing Webhook
You can directly change the status of incidents you received in Jandi channels.
Go to Extension -> Extension Settings and tab the detail page of Jandi.
![]()
From the selected extension page, copy the Status Change URL and paste it in the input field of Jandi Outgoing Webhook configuration page.
![]()
Click [Add Integration], and then you see that the Outgoing webhook has been added to your channel.
You can directly change an incident status into acknowledge or close in the Jandi channel.
Extension Settings
It allows you to perform the following actions for created extensions. You can modify, copy and delete your extensions in the same way regardless of extension types.
Modify Extension
Click Modify button in the setting page.
![]()
Change items you want to modify and click OK button.
![]()
Copy Extension
Copy extensions to other services.
Click Copy button at the right of the setting screen.
![]()
Select a service to copy extension and click OK button. You also need to change an extension name.
![]()
In Slack channel authorization screen, select a channel to post to, and click Allow button.
![]()
You can see the same extension in the service list you reset.
Delete Extension
Click Delete button at the right of the setting screen.
![]()
In delete extension screen, click the OK button to delete an extension.
![]()
Re-authorize Extension
Re-authorize Extension only applies to Slack, and to change Slack channel, you must authorize the Slack channel again.
Click Re-authorize button at the right of the setting screen.
![]()
In Slack channel authorization screen, change the channel and click Allow button.
![]()
You can see the changed channel in Slack channel of the setting item.
Teams
Team is a service for managing all the information related to incidents such as escalations, users (escalation responders) and services in a group. It also enables privacy settings to restrict access to other uses to your team.
Click Teams menu.
![]()
The Teams menu consists of the following.
![]()
| Screen Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| Team Name | The team name is displayed along with its privacy. |
| Dropdown menu | All My teams Other teams Unassigned |
- If you select a specific team from the dropdown menu, the items included in that team will be filtered out in each menu. However, the Personal Settings menu is excluded from the menu.
![]()
![]()
Add Teams
Click [Create Team].
![]()
The input items of the popup window are as follows.
![]()
| Item | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Enter a team name. | Required |
| Escalation Policy | Select escalations that need to be added to a team. | Optional |
| Team Privacy | Select the privacy for your team. Default is set to public. | Required |
| Description | Enter the description about your team. | Optional |
- Click OK to add the team.
Team Settings
Click a created team.
The detail page will be displayed as below.
![]()
Team Privacy
- Set the privacy for your team.
Public: Available for all users
Private: Available only for team members and managers
- Enable or disable the toggle button to change the team privacy.
![]()
Users
The responders included in escalations for your team will automatically be added.
Click [Modify User] to add a user. Select a user to add, and click [OK] button.
![]()
In the [Modify User] page, click the [Delete] icon to delete users. However, you cannot delete the users included in escalations.
![]()
Escalations
Click [Modify Escalation] to add an escalation. Select an escalation to add, and click [OK] button.
![]()
When adding an escalation, incidents, schedules and users that are related to the escalation will also be added to your team.
Click Exclude Escalation to disconnect the escalation from the team.
![]()
Services
A list of services that include escalations for your team will be displayed.

Delete Teams
Click a created team.
Click [Delete] from the detail page.
![]()
Click [Delete] button to delete the team. Users can assign escalation rules included in the existing team to another team before deleting it. If you select a team from [Reassign team to escalations] and click [Delete] button, the escalation rule assigned to the existing team will be reassigned to the newly selected team.
![]()
Users
Display a list of users who can receive notifications sent by AlertNow. If a user is listed here without signing in, this user can receive notifications as well. User roles and permissions are listed below.
| User Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Admin | Has overall permission to manage entire AlertNow services, and can create, modify, delete, and view Integrations, Services, Escalations, Extensions, and Incidents. |
| Responder | Is the main assignee who handles incidents after receiving alerts. Responders can view Services, Escalations, and Extensions, and create, modify, and view Incidents as well. |
| Service Manager | Can assign responders to handle incidents. |
| Observer | Can check incident status if required, and only view Services, Escalations, and Incidents. |
Change History
Change History lists the changes made to AlertNow service, who made the changes, and when each change was made. It also allows you to check all change histories for the selected period, and filter the results by the service type or change type.

Change History Configuration
It allows you to check all of changed histories for the selected period, and filter the history logs by the service type or change type.

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Select Period | Select the period to view change histories. You can select a period from Recent 1 Week, Recent 1 Month, Recent 3 Months, or Custom options. |
| Service Type | Filter change histories by service type. |
| Change Type | Filter change histories by change type. |
| Details | Display the detailed information about change histories. |
| Updated | Display the date and time of changes made. |
Notification History
Notification History provides a history of SMS and Voice calls sent by AlertNow. At the top of the page, you can see the total number of notifications offered and used by your company. You can also check the notification history sent by users in the table.

Report
System Report
System Report visualizes incident-related data via graph and table. It helps you to analyze failures more efficiently and measure performances. Thus, the report contributes to improving the service quality.
With the system report, users can check the number of incidents by escalation and service, average time to acknowledge and close incidents, and the number of escalated incidents at a glance. In addition, you can check a list of incidents belonging to the selected services and escalations, and download the information about selected incidents in a CSV file.

System Report Configuration
For system reports, you can check incident data by service and escalation.
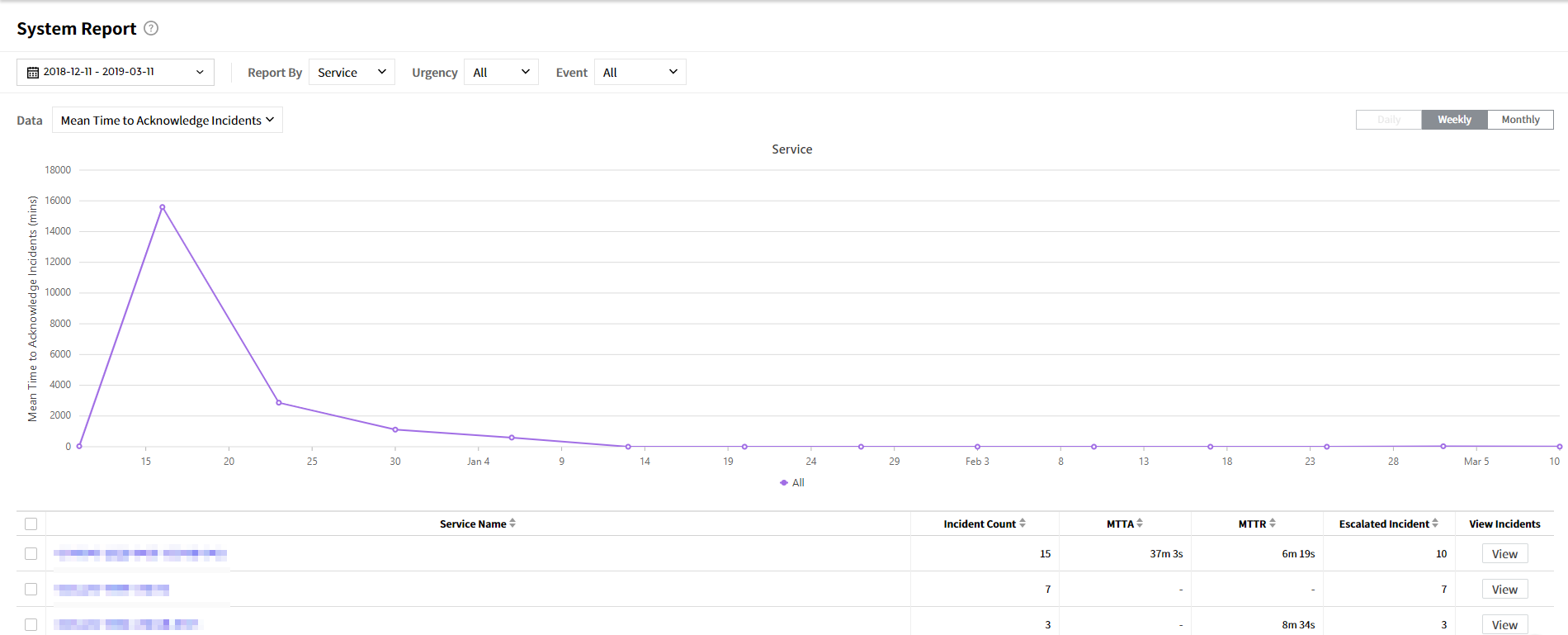
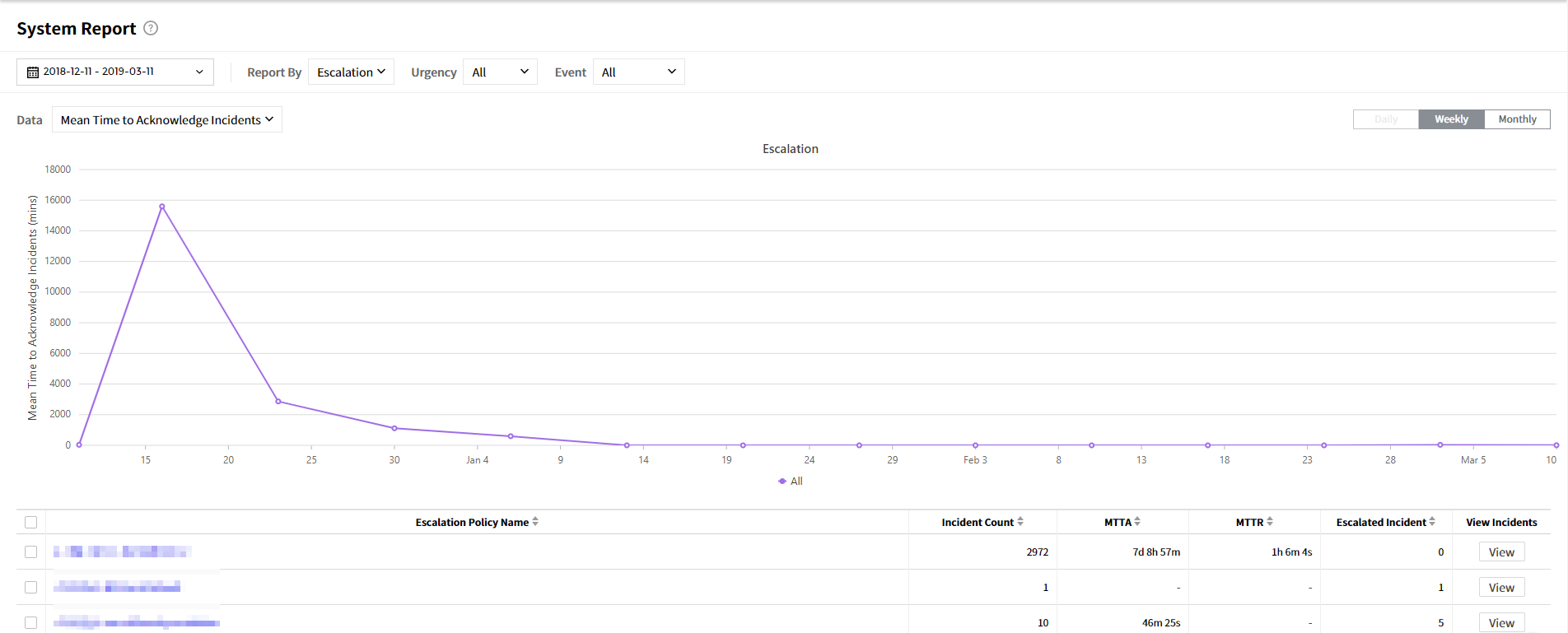
Graph
① Select Periods: Select the period to view the report. You can select a period from Recent 1 Week, Recent 1 Month, Recent 3 Months, or Custom options.
② Report By: Select the menu to view report by Escalation or Service.
③ Data: Select the data to display on a graph. You can check the number of incidents and the average time to acknowledge and close incidents.
④ Urgency: You can see the incident data by urgency, All is selected by default.
⑤ View report options: You can set the x-axis on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
⑥ Event: You can check a list of services and escalations by each of the following items.
- Escalated: Display a list of escalated incidents
- Reassigned: Display a list of incidents which assignee has been changed
- Still Open: Display a list of opened incidents
Table
① Escalation/Service: A list of escalations and services will be displayed. If you click the name, the details of escalation or service will be displayed.
② Incident Count: Display all of the incidents for the selected period.
③ MTTA (Mean Time to Acknowledge): Average time from opening to acknowledging incidents.
④ MTTR (Mean Time to Resolve): Average time from acknowledging to closing incidents.
⑤ Escalated Incident: Display the number of incidents that are escalated until the incidents closed.
⑥ View Incidents: Click the View button to go to the incident details screen.
- Select the checkbox on the left of the table to view the incident data for selected services and escalations.

View Incidents
In the incident detail page, you can check a list of incidents of selected services and escalations, and download the incident data in a CSV file. Click the View button in a report table to go to the incident detail page.

- The detail page is consisted of the following items:
![Details screen when clicking view incidents]()
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| No. | Incident number is displayed. |
| Created | The created time of incidents is displayed. |
| Time to Ack | The time from opening to acknowledging incidents is displayed. |
| Time to Close | The time from acknowledging to closing incidents is displayed. |
| Closed By | The user who closed the incident is displayed. |
| Escalation Count | The escalated incident count is displayed. |
- Click the Download CSV button to download the incident data.
Display items in CSV file
① Incident No.: Incident number
② Incident/Service/Escalation Policy Name: Names of incident, service, and escalation
③ Created: The date and time of incidents created
④ Closed: The date and time of incidents closed (It will be displayed as “-” if it is not closed)
⑤ Time to Acknowledge/Close: The time to acknowledge and close incidents (Displayed in seconds)
⑥ Acknowledged/Closed by: The user who acknowledged/closed incidents
⑦ Auto Closed: Displays whether the incident has been automatically closed (in Y/N)
⑧ Escalation Count: The number of incidents escalated
⑨ Assignment Count: The number of incidents assigned
⑩ Assignee: The one who is in charge of handling incidents
⑪ Urgency: Displays incident urgency
Incident Report
Incident Report enables you to gain insights by analyzing incident trends and providing metrics based on service, integration, and urgency. It helps you to predict the occurrence of incidents based on old data and prevent the occurrence of incidents by service in advance. Incident Report enables you to check the number of incidents and alerts occurred for the selected period and view the overall incident analysis chart and data.
Start by clicking Analytics > Incident Report.

Incident Report Configuration
Incident Report allows you to check the metrics for a selected period such as total number of incidents opened, number of still opened incidents and number of alerts occurred. In addition, you can check the incident charts by service, integration, urgency, the incident trend, and the trend of both open and acknowledged incidents.
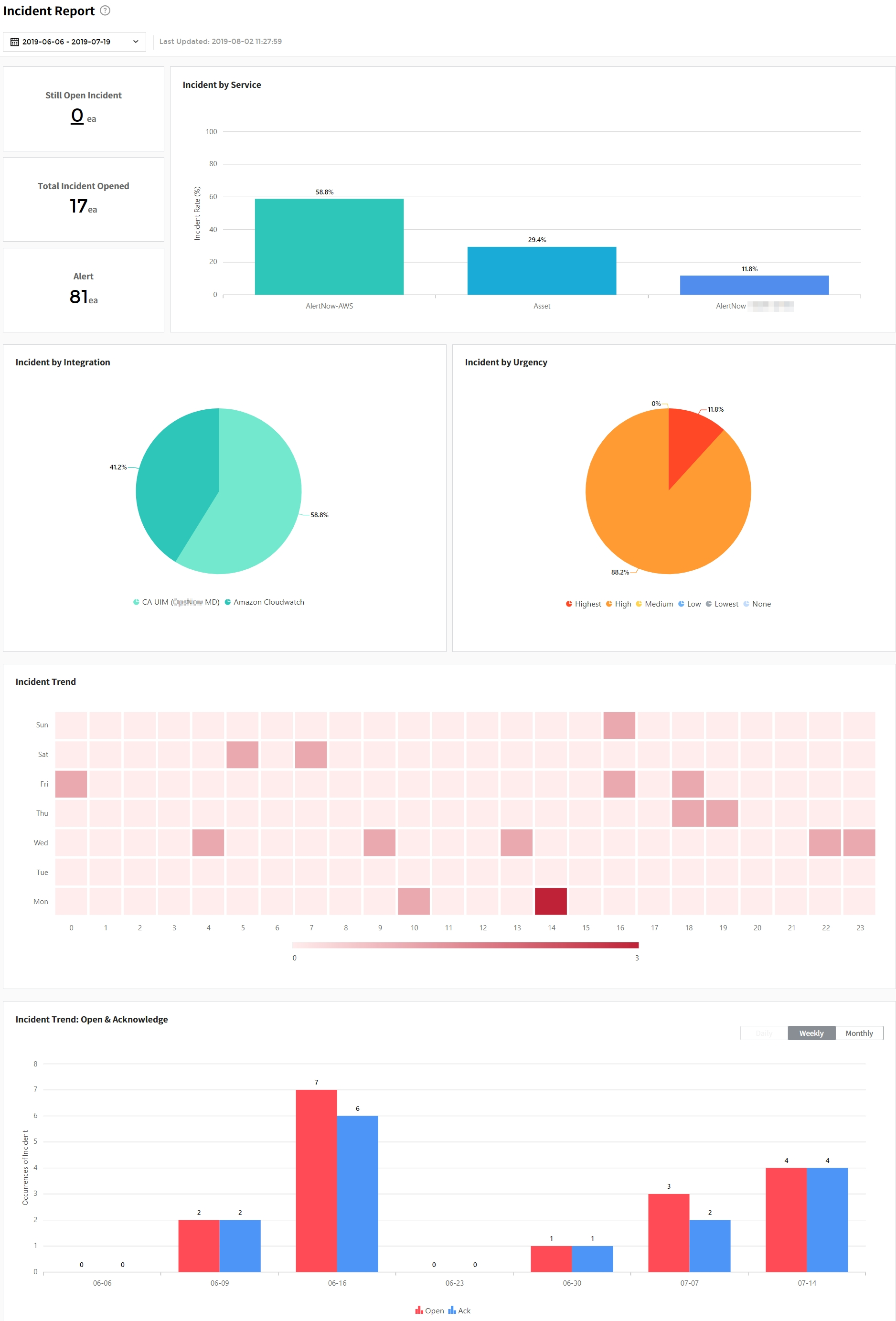
Graph
① Select Period: Select the period to view the report. You can select a period from Recent 1 Week, Recent 1 Month, Recent 3 Months, or Custom options.
② Incident by Service: This bar chart shows the occurrences of incident by service for the selected period. The x-axis represents the service and the y-axis represents the incident rate.
③ Incident by Integration: This pie chart shows the occurrences of incident by integration for the selected period.
④ Incident by Urgency: This pie chart shows the occurrences of incident by urgency for the selected period. Urgency is divided into 6 types: Highest, High, Medium, Low, Lowest and None.
⑤ Incident Trend: This chart shows the incident trend for the selected period. The x-axis represents the time ranging from 0:00 to 23:00 and y-axis represents the day of the week. It also shows the occurrences of incidents ranging from 0 to 9 with brightness variations.
⑥ Trend of Incident Open & Acknowledge: This bar chart shows the trend of open and acknowledge incidents for the selected period. The x-axis represents the date and y-axis represents the number of incidents occurred. You can set the x-axis on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis. Duration of the following table varies based on an option selected. Daily option becomes inactive when the duration is set to 35 days or more.
Table
① Duration: Displays the duration depending on selected options from daily, weekly or monthly.
② Incident Count: Displays the total incidents for the selected period.
③ View Incidents: Click the [View] button, it goes to the incident details screen.

View Incidents
From the incident details screen, you can check a list of incidents for the selected period, and download the incident data in a CSV file. Click the [View] button in a report table to go to the incident details screen.

It consists of the following items:

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| No. | Incident number is displayed. |
| Created | The created time of incidents is displayed. |
| Time to Ack | The time from opening to acknowledging incidents is displayed. |
| Time to Close | The time from acknowledging to closing incidents is displayed. |
| Closed By | The user who closed the incident is displayed. |
| Escalation Count | The escalated incident count is displayed. |
- Click the [Download CSV] button to download the incident data.
Display items in CSV file
① Incident No.: Incident number
② Incident/Service/Escalation Policy Name: Names of incident, service, and escalation
③ Created: The date and time of incidents created
④ Closed: The date and time of incidents closed (It will be displayed as “-” if it is not closed)
⑤ Time to Acknowledge/Close: The time to acknowledge and close incidents (Displayed in seconds)
⑥ Acknowledged/Closed by: The user who acknowledged/closed incidents
⑦ Auto Closed: Whether the incident has been automatically closed (in Y/N)
⑧ Escalation Count: The number of incidents escalated
⑨ Assignment Count: The number of incidents assigned
⑩ Assignee: The one who is in charge of handling incidents
⑪ Urgency: Incident urgency
Notification Report
Notification Report provides visualized data and graphs about notifications that are sent to users for a specified period. It also allows you to check detailed information like total number of notifications and number of notifications that are sent by notification types. Users can view detailed data by looking at the number of notifications that are sent based on a date or type over a specified period.

Notification Report Configuration
For Notification Report, you can check the total number of notifications and notification types that are sent. In addition, the data about notification reports will be displayed by its type and date.
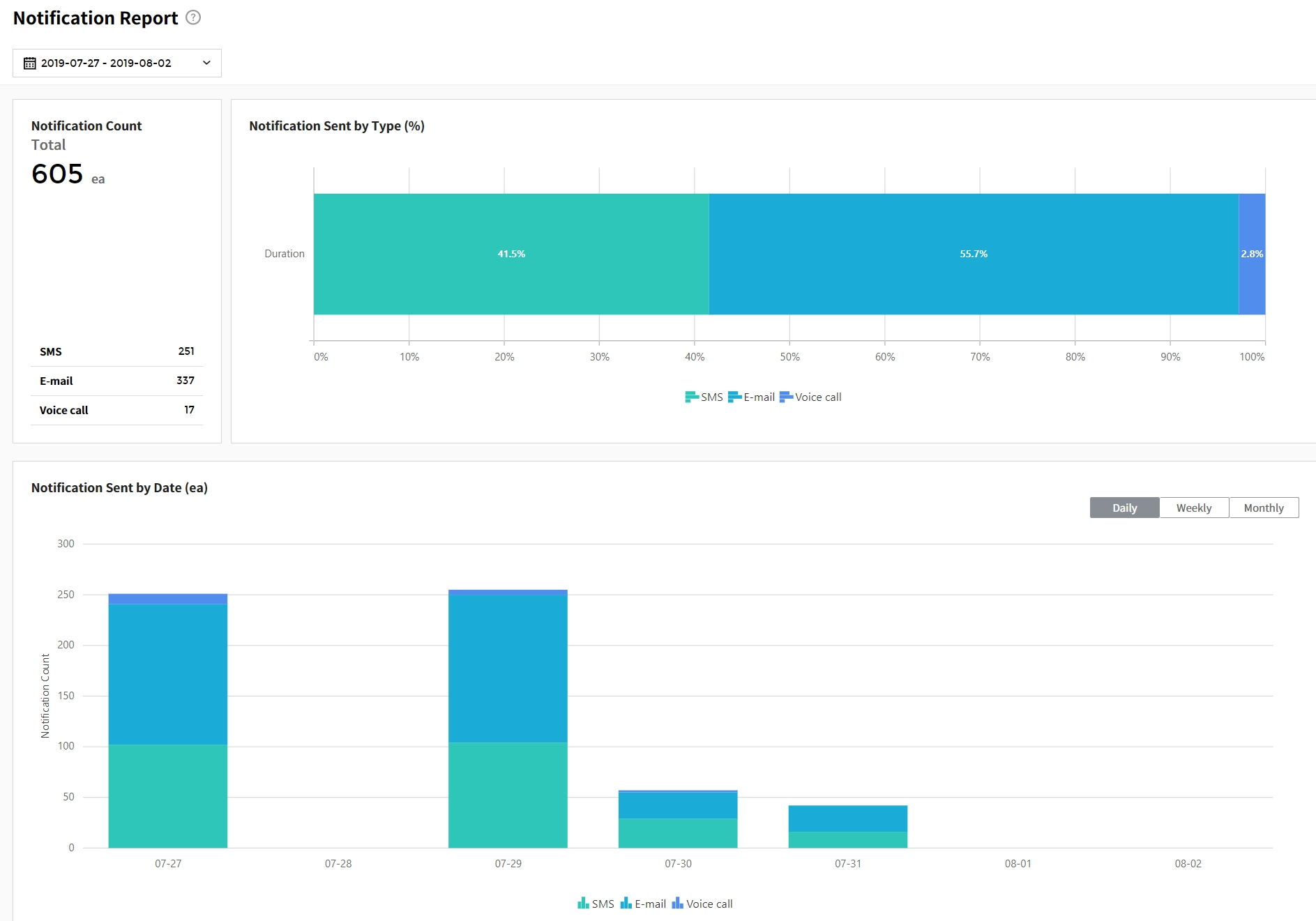
Graph
① Select Period: Select the period to view report. You can select one from Recent 1 Week, Recent 1 Month, Recent 3 Months, or Custom options.
② Notification Sent by Type: This bar chart shows the notification sent by type for the selected period. The x-axis represents the percentage of notifications sent and the y-axis represents the duration.
③ Notification Sent by Date: This bar chart shows the number of notifications sent by date for the selected period. The x-axis represents the date and y-axis represents the notification count. It also displays notification types with different colors for SMS, voice call, and email. You can set the x-axis on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis. Duration of the following table varies based on the option selected. Daily option becomes inactive when the duration is set to 35 days or more.
Table
① Duration: Displays the duration depending on selected options from daily, weekly or monthly.
② Total: Displays the total notification count for the selected period.
③ Notification Type (SMS, Voice call, Email): Displays number of notifications sent by its type for a selected period.
④ View Notification: Click the View button, it goes to the notification details screen.

View Notification
In the notification details screen, you can check a list of notifications for the selected period, and download the data in a CSV file. To go to notification details screen, click the View button in a report table.

It consists of the following items:

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Date | The date of notification sent is displayed. |
| Notification Type | The type of notification sent is displayed. |
| Contact Info | The contact information of the notification sent is displayed. |
| User | The name of users who received the notification is displayed. |
- Click the Download CSV button to download the incident data.
Display items in CSV file
① Date: The date of notification sent
② Notification Type: The type of notification sent
③ Contact Info: The contact information of notification sent
④ User: The user name of notification received
Personal Settings
Set up contact information, notification rules, roles & permissions, and user settings.
Personal Information
① You can set contact information for receiving incident notifications, and up to 5 contacts can be added. However, the free version offers 3 contacts only.

② Click Add icons to add your email address, SMS, Voice call, and KakaoTalk.

Notification Settings
Set up to receive incident notifications via SMS, Email, Voice Call, KakaoTalk, and WeChat based on user-defined rules.
SMS notifications
※ Calling numbers may vary depending on national restrictions.
① Choose SMS from the dropdown menu, and select checkboxes for receiving notifications and click [Save] button.

② If you select [Escalation] checkbox, you will receive SMS notifications when an incident is created for escalations configured in Additional Information.

- Reply to SMS by Item
| No. | Item | 2-way | 1-way |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Incident Number | O | O |
| 2 | Service Name | O | O |
| 3 | Incident Name | O | O |
| 4 | The number to change incident status to ‘Acknowledged’ (ends with 1) | O | X |
| 5 | The number to change incident status to ‘Closed’ (ends with 3) | O | X |
③ If you select Assign checkbox, you will be assigned as the manager and receive notifications as below.

④ If you reply by pressing the number to change incident status to Acknowledged, you will receive SMS notifications as below.

⑤ If you reply by pressing the number to change incident status to Closed, you will receive SMS notifications as below.

⑥ The support policy for sending and receiving SMS texts per country is as follows.
| SMS | |
|---|---|
| Korea | 2-way |
| China | 2-way |
| USA | 2-way |
| Canada | 2-way |
| Poland | 1-way |
| Philippines | 1-way |
| India | 1-way |
| Vietnam | 1-way |
| German | 2-way |
| Saudi Arabia | 1-way |
| United Arab Emirates | 2-way |
| Singapore | 2-way |
| Brazil | 2-way |
- One-Way: You can only receive incident notifications via SMS.
- Two-Way: You can receive incident notifications and reply to change the status of incidents.
📑 Note: While users in multiple countries can receive SMS notifications, there are some countries where responders may be unable to reply to these notifications due to supported environments and several factors. You may experience problems when you reply to the notification message depending on your carrier.
Email notifications
① Choose Email from the dropdown menu, and select checkboxes to receive notifications and click [Save] button.

② When an incident is created, you will receive notifications via email.

③ For email, you should manually change incident status (Acknowledge/Close) and its assignee in the incident detail page in order to receive notifications.

Voice Call notifications
※ Depending on the situation of telecommunication carriers in the country or region, the calling numbers may change, lower reception rates, or the reception status indicators may be different.
① In Personal Info > Voice Call, click [+ Add Voice Call].
② Enter your contact information for receiving notifications and click [Save] button.

③ In Voice call notification settings, click [+ Add Voice Call Notification].
④ Your contact information will be automatically displayed. Select the contact and click [Save] button. In order to receive voice call notifications, you must be included in the escalation responder list.

⑤ The voice call messages are supported in Korean and English only, and the contents are as follows.
| Item | Language | Voice message |
|---|---|---|
| If an incident occurs (2-way) | English | This is an AlertNow notification. You have an incident on {service name} service. The incident number is {incident number}. To acknowledge incidents, please press {Number}. To close incidents, please press {Number}. To repeat the message, please press {*}. |
| If an incident occurs (2-way) | Korean | 얼럿나우 알림입니다. {service name} 서비스에 인시던트가 생성되었습니다. 인시던트 번호는 {incident number}입니다. 인시던트를 확인하시려면 숫자 일번을, 종료 하시려면 숫자 이번을 누르세요. 메시지를 반복하려면 별표를 누르세요. |
| If an incident occurs (1-way) | English | This is an AlertNow notification. You have an incident on {service name} service. The incident number is {incident number}. |
| If an incident occurs (1-way) | Korean | 얼럿나우 알림입니다. {service name}에 인시던트가 생성되었습니다. 인시던트 번호는 {incident number}입니다. |
※ The number of sending and receiving voice calls may differ depending on your carrier.
⑥ The support policy for receiving Voice Call service per country is as follows.
| Voice Call | |
|---|---|
| Korea | 2-way |
| USA | 2-way |
| Canada | 2-way |
| Poland | 2-way |
| Philippines | 1-way |
| India | 1-way |
| Vietnam | 1-way |
| German | 2-way |
| Saudi Arabia | 1-way |
| United Arab Emirates | 1-way |
| Singapore | 1-way |
| Brazil | 1-way |
- One-Way: You can only receive incident notifications via Voice Call.
- Two-Way: You can receive incident notifications and change incident status during the call.
📑 Note: There are some countries where users may be unable to respond to these voice call notifications, due to supported environments and other factors.
WeChat notifications
※ Depending on your country or region, this feature may not be available.
① Choose WeChat, and select checkboxes to receive notifications and click the check button.

② Like SMS, you will receive a message displayed below when an incident is created for escalations configured in Additional Information.

③ If notification is escalated, you will receive a message as below.

④ If no one acknowledges notifications for any of the escalation steps, you will receive an escalation reminder message as below.

⑤ If incident status is changed to either Acknowledge or Close, you will receive a status change message as below.

⑥ If an incident assignee is changed, you will receive assignee change as below, and changed assignee will be displayed in “Assignee”.

Notification Rules
Users can configure notification rules to receive notifications based on user-defined rules.
① Click [+ Add Notification Rule] button.

② Enter a notification rule name and select an event to apply. You can use [+ Add] button to add more events.

③ Configure conditions to apply. You can use [+ Add] button to add more conditions.

④ Click [OK] button to add a notification rule.
Notification Restrictions
Restriction to Time Intervals
Users can specify the time of the day or the duration of the week in order not to receive notifications. During the specified hours or the specified day, Alertnow will not send notifications to the user.
Click [+ Add Restriction to Time Intervals] button.
![]()
Select one from Daily or Weekly option. Specify hours of the day or the duration of the week and click [Add] button. If you choose Daily and set the time to 09:00~12:00, you will not receive any notifications during the specified hours everyday. For Weekly, if you set a date to Monday and time to 09:00~12:00, you will not receive any notifications during those hours every Monday.
![]()
Click [OK] button to add a restriction to time intervals.
![]()
Mute Notifications
Users can mute notifications for a specified time. If you enable this option, you will not receive any notifications during the specified time.
0 is set as a default setting. Click [Modify] button to add a desired time period for mute, but note that the time can be added at a maximum of 1440 minutes.
![]()
Click [Save] button to complete the setting.
![]()
You can change the specified time using the [Modify] button or delete it by clicking the [Delete] button.
![]()
Notification Forwarding Rules
When users may not be able to receive notifications, AlertNow allows you to create a notification forwarding rule to forward your notifications to another user for a specified time frame. You can add up to 5 notification forwarding rules.
Click [+ Add Notification Forwarding Rule].
![]()
Select a responder to forward notifications, and specify the start time and end time.
![]()
Click [Save] button to add a notification forwarding rule.
Notification forwarding rules added by me
If you cannot receive notifications, you can assign other users to receive notifications for you for a specified time period. Click [Notification Forwarding Rule] to specify a responder and start & end times to create a rule.

Notification forwarding rules added to me
Others can assign you to receive notifications for them by adding [Notification Forwarding Rule]. When someone adds you to a Notification forwarding rule, you can check notifications you will receive and who will assign you for these notifications as well.

Mobile Notification Settings
Mobile notification can be set both on the web and the app. You can set up notifications to receive incident notifications in mobile apps in one of two ways:
On the Web
① Click [+ Add Notifications] button in the Default Notifications of Personal Settings.

② Select Mobile App from the dropdown menu, and select checkboxes for receiving notifications and click the Save button.

③ When you select [Escalation] checkbox, you will receive notifications on your mobile app when an incident is created.
④ When you select [Assign] checkbox, you will receive notifications on your mobile app when you are added as a responder for an incident.
On the App
To receive notifications, turn on push notification on your mobile app.

- Mobile App Status
① You can view the current status of mobile apps connected to your account.

② Divide can be deleted, however if you delete a device, you cannot receive notifications on your app and your device will be deactivated.

Additional Information
① The additional information items are as follows.

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Zone | Users can change the time zone to a desired one. By default, the time zone is set to the browser time. |
| Language | Users can set a language preference. Supported languages are Korean, English, Chinese, and Japanese. |
| Default Permission | Information about AlertNow roles that the user belongs to: Admin, Manager, Responder, and Observer |
| Teams | Display a list of teams that the user belongs to or created. |
| Escalations | Display a list of escalations that the user belongs to or created. |
| Schedules | Display a list of schedules that the user belongs to or created. |
Mobile App
AlertNow mobile app is available on the Apple App Store and Google Play. You can receive notifications on your mobile app, and acknowledge or close incidents as well. Also, you can assign or change a responder.
Getting Started
① When you open the AlertNow app for the first time, you will be prompted to enter your email address to login.

② Enter your email and select service territory, and then tap Next button.
③ Select a domain to login and tap OK button.

④ Enter your password to login.
If you enabled the Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) feature in Additional Security Settings of My Account, you need to enter MFA authentication numbers to login.

⑤ After login, you can see incidents. The All tab shows all open and acknowledged incidents in the account. The Open tab shows open incidents only, and you can filter incidents by My Team. You can also see incidents that are assigned to your teams.

Acknowledging Incidents
① Open incidents will be under the Open Incidents tab.

② You can acknowledge an incident by tapping the incident and tapping the [Acknowledge] button on the incident details page.

Closing Incidents
To close an open or acknowledged incident, tap the incident.

Tap the [Close] button on the incident details page.

Adding and Changing Assignee
You can add or change incident assignees.
Add Assignee
Go to the incident you want to assign and tap > button.
![]()
Search for an assignee. Tap the name of the person you want to assign.
![]()
Change Assignee
Go to the incident you want to reassign and tap > button.
![]()
Search for an assignee. Tap the name of the person you want to reassign.
![]()
Notification settings
- Push Notifications
To receive incident notifications from AlertNow on your app, turn on push notifications in Personal Settings > Notifications.

- Wake Notifications
To receive incident notifications from AlertNow, turn on wake notifications in Personal Settings > Notifications. Just like Voice Call, the system will call you on your cell phone to notify you whenever alarms are triggered. When you press the call button, the system thinks that you received the notification, and the call is ended.






























































































































































































































































































































































